FIGURE 1.
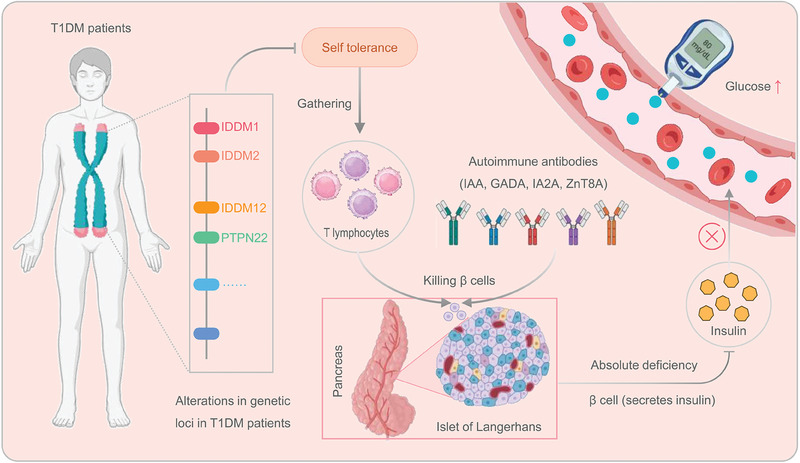
The immune mechanisms of T1DM. In individuals with T1DM, the immune tolerance is disrupted due to genetic alterations in specific loci, such as IDDM1, IDDM2, IDDM12, and PTPN22, among others. The defective immune tolerance leads to the proliferation of T lymphocytes and the targeting of pancreatic islet beta cells by immune cells and autoantibodies (such as IAA, GADA, IA2A, and ZnT8A). This attack destroys pancreatic islet beta cells, leading to a deficiency of insulin and subsequent elevation of blood glucose levels. GADA, glutamic acid decarboxylase; Glu, glutamate; IA2A, insulinoma‐associated antigen; IAA, insulin autoantibodies; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; ZnT8A, zinc transporter 8.
