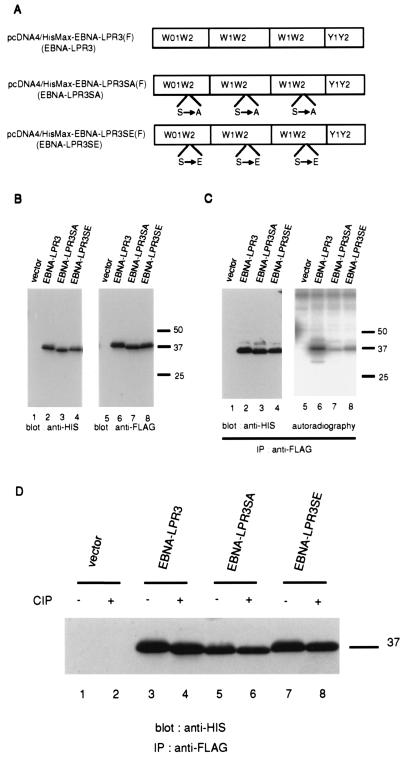
FIG. 5.
(A) Schematic representation of FLAG epitope-tagged wild-type EBNA-LP and EBNA-LP mutants with serine-alanine and serine-glutamic acid substitutions at the identified phosphorylation site. (B) Photographic images of immunoblots of electrophoretically separated lysates of BOSC23 cells transiently transfected with the empty vector and the expression vectors shown in panel A, harvested, solubilized, electrophoretically separated in denaturing gels, and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-His polyclonal antibody (H15) (left panel) or anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (M2) (right panel). Molecular weights, given in thousands, are shown on the right. (C) Autoradiogram (left panel) and photograph of an immunoblot (right panel) of 32P-labeled proteins immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody from lysates of BOSC23 cells transiently transfected with the indicated expression vectors. Experiments were done exactly as described in the legend to Fig. 4C, except that BOSC23 cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors and the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (M2). Molecular weights, given in thousands, are shown on the right. (D) Photographic image of an immunoblot of proteins immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (M2) from lysates of transfected BOSC23 cells, treated with alkaline phosphatase as described in Materials and Methods, electrophoretically separated in a denaturing gel, transferred to a nitrocellulose sheet, and reacted with anti-His polyclonal antibody (H15). BOSC23 cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors, harvested, and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-HIS polyclonal antibody (H15). A molecular weight marker, given in thousands, is shown on the right.