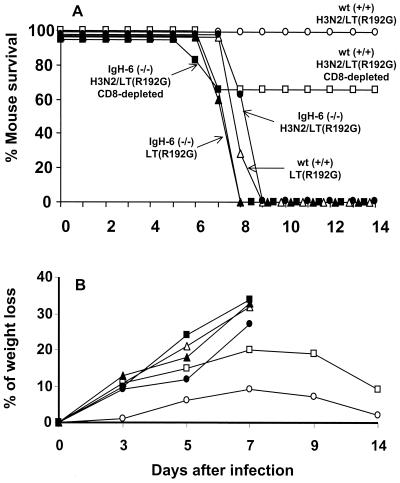
FIG. 4.
Susceptibility of B-cell-deficient mice to heterosubtypic challenge. Four groups (eight per group) of mice were vaccinated i.n. three times with H3N2/LT(R192G) vaccine at weekly intervals. The immunized groups of IgH-6−/− (■) and wt (□) control mice were treated with 1 mg of anti-CD8 (clone 2.43) ascites on days −2, +2, and +6 relative to the time of virus challenge. In addition, immunized groups of IgH-6−/− (●) and wt (○) mice received control ascites (clone SFR3-DR5) in place of anti-CD8 MAb. Control wt (▵) and IgH-6−/− (▴) mice received LT(R192G) adjuvant only. Two weeks after the final vaccine boost, mice received a lethal heterosubtypic challenge with 100 MID50 of H5N1 virus. Blood samples were collected from the orbital plexus on day 3 p.c. from all mice and were tested for the presence of serum IgG and IgA antiviral titers by ELISA and HAI as described in Materials and Methods. No IgG, IgA, or HAI antibodies could be detected in IgH-6−/− H3N2-immunized mice, whereas wt-immunized mice had mean HAI titers of 2,560 and IgA or IgG serum titers of ≥64,000 to X-31 virus. In addition, two mice from each group were euthanatized on day 3 p.c. to confirm depletion of CD8+ T cells and/or CD45R/B220+ B cells by flow cytometry. Cells from the spleen were analyzed for CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD45R/B220+ B cells as described in Materials and Methods. Anti-CD8 treatment resulted in more than 95% reduction of the T-cell subpopulation in IgH-6−/− (■) and wt (□) mice. Analysis of CD45R/B220+ B cells in the wt mice revealed a normal range (55 to 65%) of spleen cells in comparison to 1.9 to 2.2% detected in IgH-6−/− mice.