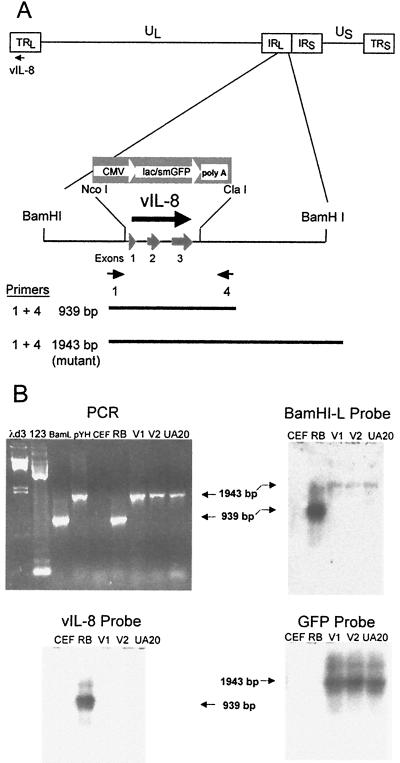
FIG. 7.
Structural characterization of RB1BvIL-8ΔsmGFP. (A) Schematic diagram of the MDV genome showing the region expressing the vIL-8 gene, the restriction sites used in the deletion of vIL-8, the smGFP expression cassette used in mutagenesis, and the location of PCR primers used in the structural characterization of the parental and mutant viruses. (B) An agarose gel showing the results of PCR amplification using primers 1 and 4 (shown in panel A) (upper left panel) and Southern blot hybridization analysis of these products using the BamHI-L fragment of the MDV genome (upper right panel), the vIL-8 cDNA (lower left panel), and the smGFP gene (lower right panel) as probes. The lanes are λd3, HindIII-digested lambda DNA molecular weight markers; 123, 123-bp DNA ladder markers (GIBCO-BRL); BamL, pUC19 containing the BamHI-L fragment of the MDV genome (20); pYH, transfer vector pYH6a; CEF, uninfected CEF DNA; RB, RB1B parental MDV-infected CEF DNA; V1, RB1BvIL-8ΔsmGFP clone 2-infected CEF DNA; V2, RB1BvIL-8ΔsmGFP reisolated from spleen cells of infected chickens; and UA20, DNA from cell line MDCC-UA20, established from an RB1BvIL-8ΔsmGFP-induced ovarian lymphoma.