Figure 3.
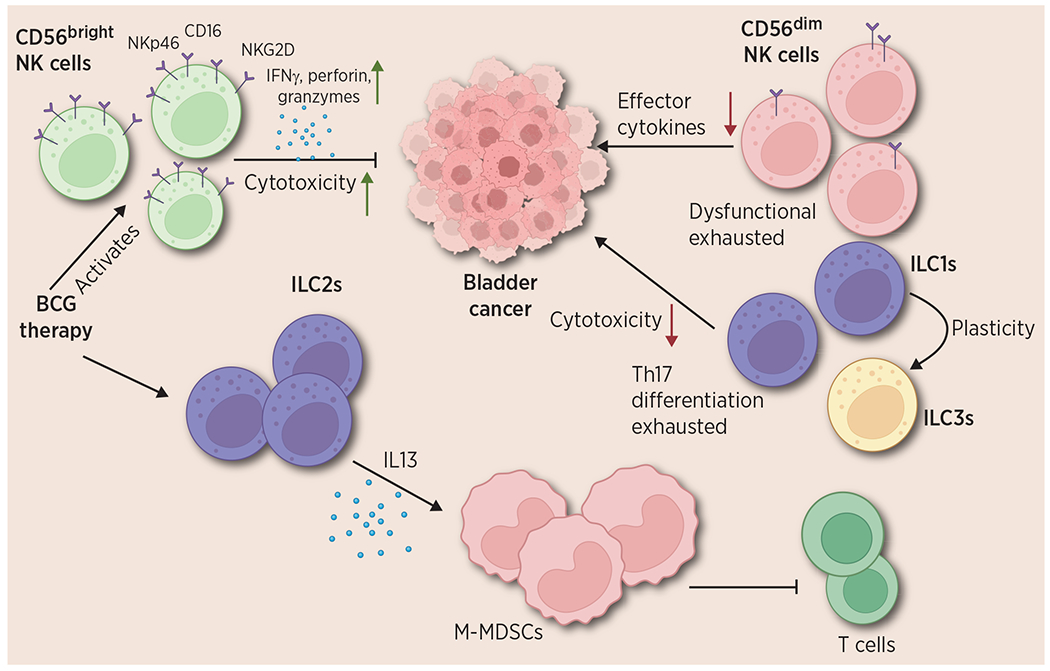
Functions of ILCs in bladder cancer. The different roles of NK cells, ILC1s, ILC2s, and ILC3s are depicted. Bladder intratumoral CD56bright NK cells show an activated phenotype with higher expression of NKp46, NKG2D, and other activation markers; they elicit antitumor functions via secretion of IFNγ, granzymes, and perforin. However, CD56dim NK cells in the tumor are dysfunctional and display an exhausted phenotype and their antitumor abilities are significantly decreased. ILC1s, also show lowered cytotoxicity and Th17 differentiation in bladder cancer. They display plasticity with ILC3s. ILC2s show a protumorigenic function in bladder cancer via IL13 mediated M-MDSCs differentiation which suppresses T-cell functions. Created with BioRender.com.
