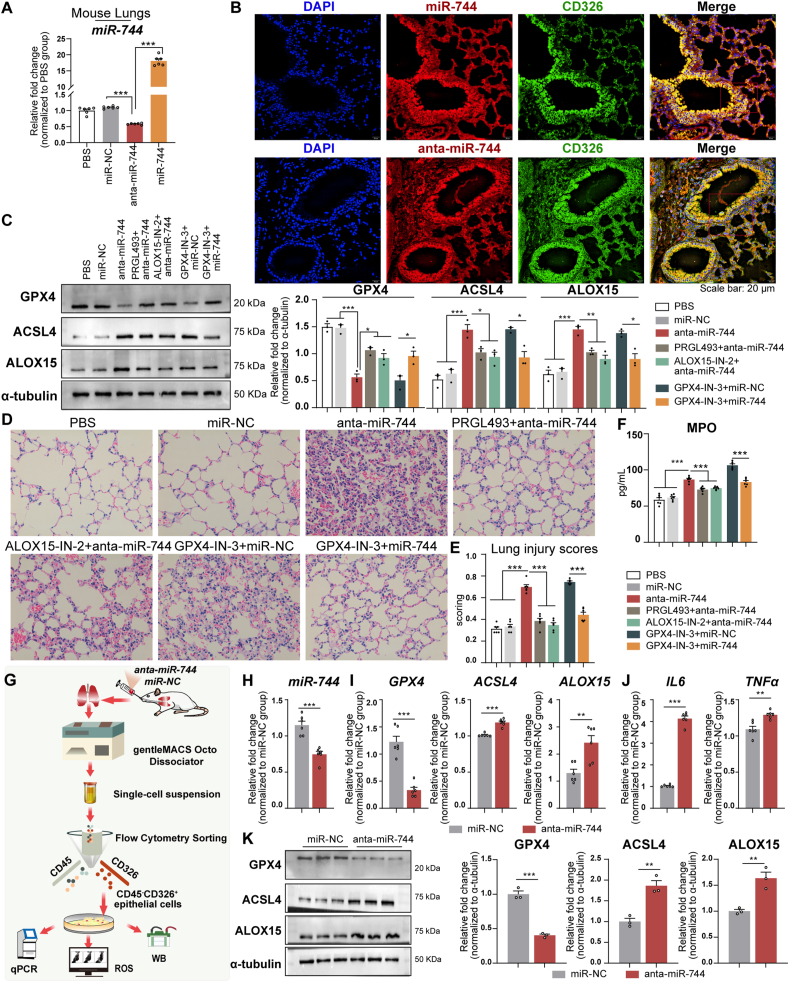
Fig. 8.
Intratracheal administration of anta-miR-744 modulated ferroptosis, inflammation, and injury in mouse lungs via GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15 regulation. (A–F) BALB/c mice were administered miR-744 or anta-miR-744 intratracheally, and lungs were analyzed after 24 h (n = 6 mice/group). (A) miR-744 expression in lung tissue. (B) Fluorescence microscopy showing epithelial uptake of miR-744/anta-miR-744. (C) Left panel: Representative western blots for GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15; Right panel: Blots quantified using ImageJ. (D) Representative H&E staining images. (E) H&E staining results were quantified in a blinded manner to determine the lung injury scores. (F) ELISA for myeloperoxidase activity. (G) Flowchart of experiments using pulmonary epithelial cells. (H) qPCR results for miR-744 in isolated pulmonary epithelial cells. (I) qPCR results for GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15 expression. (J) qPCR results for IL6 and TNFa expression. (K) Left panel: Representative western blots for GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15; Right panel: Blots quantified using ImageJ. (A–F) ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (ANOVA, followed by multiple comparisons test); (H–K) ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). ACSL4, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4; ALOX15, 15-lipoxygenase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; HBE, human bronchial epithelial; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; miRNA, microRNA.