FIGURE 2.
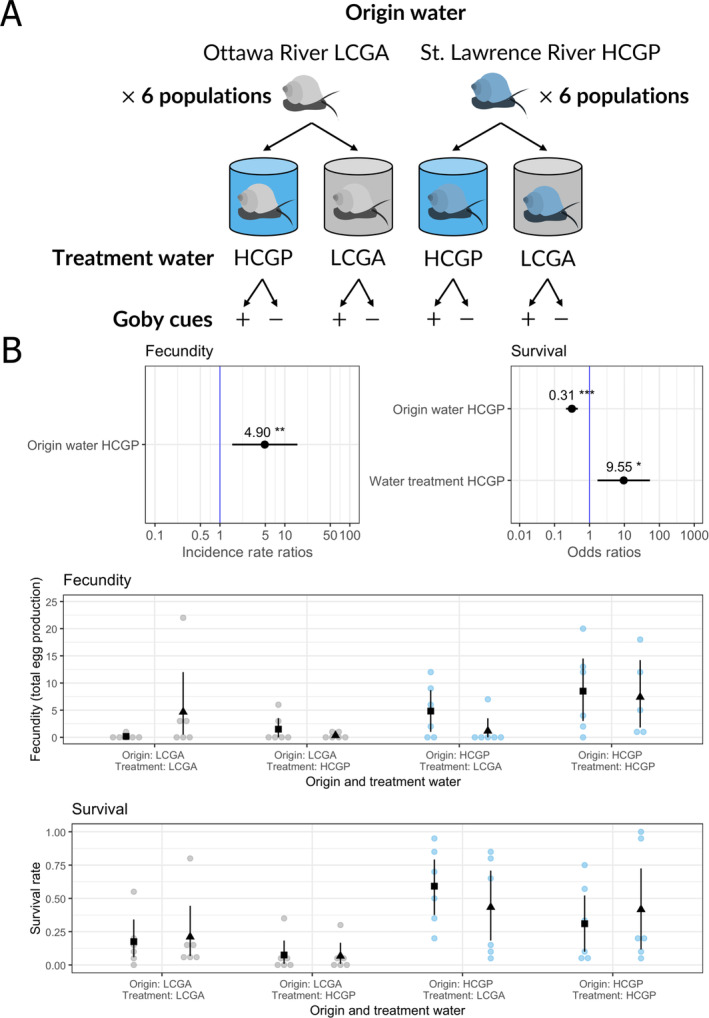
Experimental design of the laboratory reciprocal transplant experiment and results for the fecundity (total number of eggs produced) and survival of adult Amnicola limosus as a function of water treatment, origin water, and round goby cue treatment in the reciprocal transplant experiment. (A) Experimental design showing the two origin waters (Ottawa River Low Calcium/round Goby Absent LCGA in grey or St. Lawrence River High Calcium/round Goby Present HCGP in blue) with six replicate populations each, the water treatments (LCGA and HCGP) and the round goby cue treatment (+/–: With or without). (B) Top: Results of the converted coefficients of significant fixed effects (incident rate ratios and odds ratio) of the GLM and GLMM used to analyze fecundity and survival, respectively. Asterisks indicate threshold of p‐values: * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, *** for p < 0.001. Bottom: Raw data of the experiment, each dot represents a measurement for one population (origins in grey: LCGA, blue: HCGP), summarized by the mean for each treatment (black squares and triangles for treatments with or without round goby cues, respectively) and the 95% confidence interval around the mean (bootstrapping method).
