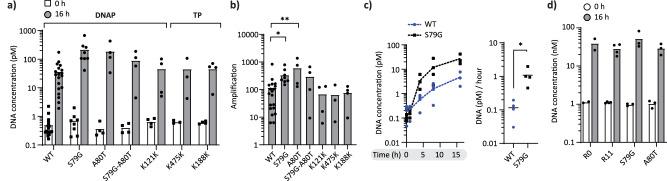
Fig. 5. Reverse engineering and characterization of fixed end-point mutations.
a Assessment of reverse-engineered self-replicator variants’ replication activity in in-liposome IVTTR by qPCR. qPCR amplicon is amplified from a p2 gene region of mod-ori-p2p3. b Self-amplification displayed as ratio of DNA concentration at 16 h to initial template concentration at 0 h in panel a. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. c Left: Comparison of in-liposome IVTTR kinetics of the parental mod-ori-p2p3 DNA template and its variant with the S79G mutation in the p2 gene. Absolute quantification of DNA was performed by qPCR (n = 3 biological replicates). Dashed lines connect the mean values of replicates. Right: Apparent maximum DNA replication rates defined as the highest slopes (between 1 and 4-h time points) in the kinetic curves. *P < 0.05. d Comparison of parental mod-orip2p3 (R0), recovered DNA from Int-WT(1) round 11, and reverse-engineered self-replicator variants’ replication activity in bulk IVTTR by qPCR. Data points are from three to 19 biological replicates, except for panel d, where condition R0 was repeated twice. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.