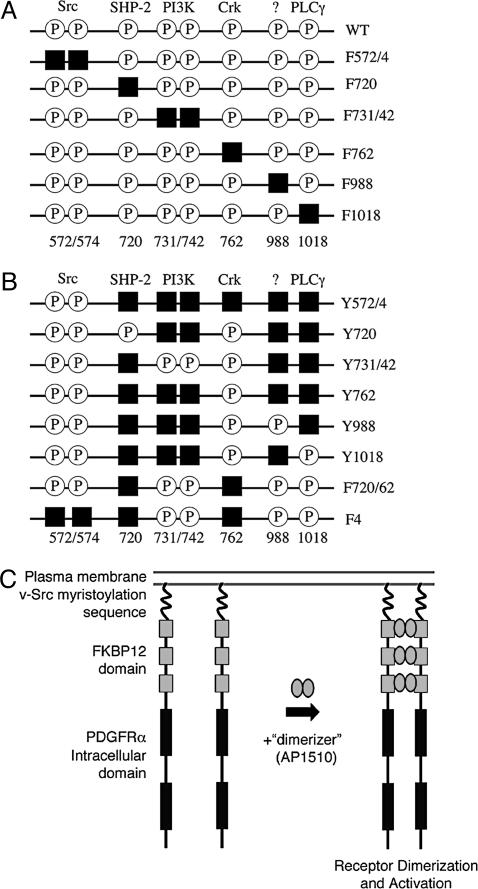
Fig. 1.
Schematic of iPDGFRα mutants. To dissect PDGFRα signaling, tyrosines that when phosphorylated (P) bind and activate specific downstream effectors were replaced by phenylalanine (black squares) by site-directed mutagenesis. (A) Subtraction mutants contain mutations that allow binding and activation of all but one downstream effector. (B) Add-back mutants contain mutations to allow binding and activation of one or more downstream effector. (C) iPDGFRα is a fusion protein of the myristoylation signal from v-Src, three tandem repeats of FKBP12 containing point mutations G89P and I90K to block calcineurin binding, and the cytoplasmic domain of the PDGFRα with or without specific Y→F mutations. The addition of the dimerizer, AP1510, activates the receptor kinase through the induced dimerization of two of the receptor fusion proteins.