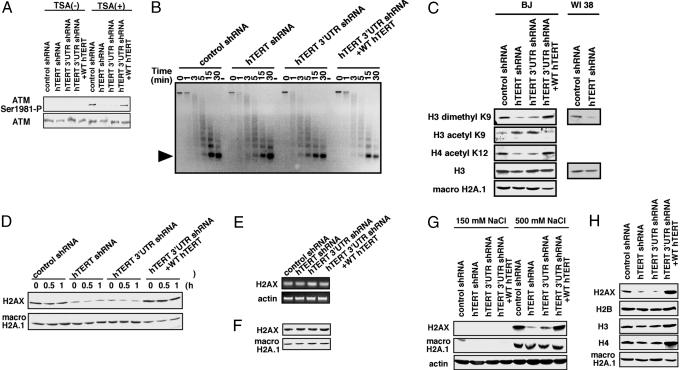
Fig. 3.
Suppressing hTERT expression alters chromatin state. (A) Effects of hTERT suppression on chromatin alterations induced by TSA. Cells were treated with TSA (10 μM) for 8 h. Phosphorylated ATM and total ATM protein levels were determined by immunoblotting. (B) MN digestion of nuclei derived from cells expressing the indicated shRNA vectors. Nuclei isolated from 1 × 106 cells were treated with MN for the indicated time, subjected to gel electrophoresis, and stained with ethidium bromide. The arrowhead indicates the migration of mononucleosomes. (C) Histone tail modifications. BJ cells expressing the indicated shRNA were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA), and immunoblotting was performed. (D) Extraction of H2AX from chromatin. BJ cells expressing the indicated shRNA were irradiated (10 Gy), incubated for the indicated time, and lysed with RIPA buffer, and immunoblotting was performed on whole cell lysates (100 μg). (E) H2AX mRNA expression. Total RNA (500 ng) was used for RT-PCR with primers specific for H2AX and β-actin. (F) Precipitation of H2AX from chromatin under acidic conditions from BJ cells expressing the indicated shRNA vectors. (G) Extraction of histones under low and high ionic strength. Cells were lysed with low salt buffer and high salt buffer and immunoblotted as indicated. (H) Extraction of core histones from chromatin. BJ cells expressing the indicated shRNA were lysed in RIPA buffer, and immunoblotting was performed on whole cell lysates (100 μg).