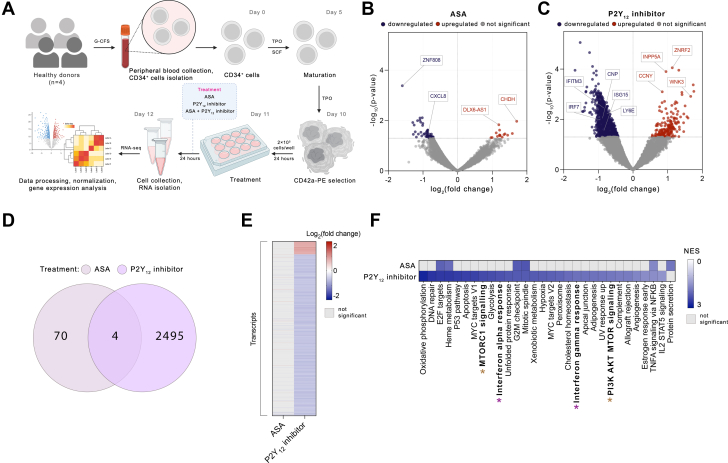
Figure 1.
P2Y12 Inhibitor, But Not ASA Suppresses IFN Signaling Pathways in MKs
(A) Experimental workflow: CD34+ cells were differentiated into megakaryocytes (MKs) for 10 days in the presence of human thrombopoietin (TPO). MKs were purified by selection of CD42a-positive cells. Purified MKs were treated with 100 μmol/L aspirin (ASA), 5 μmol/L AZD1283 (P2Y12 inhibitor), or both drugs together for 24 hours. After 24 hours, cells were collected, RNA was isolated, and RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) performed. (B, C) Volcano plots of differentially expressed transcripts of MKs treated with ASA (B) or P2Y12 inhibitor (C). Colored dots are P < 0.05; red dots represent up-regulated and blue dots down-regulated genes. (D) Venn diagram and (E) heatmap of differentially expressed genes identified in MKs treated with ASA or P2Y12 inhibitor (P < 0.05). Red color represents up-regulated and blue down-regulated genes. (F) Gene set enrichment analysis of hallmark pathways of MKs treated with ASA or P2Y12 inhibitor (P < 0.05). The purple asterisk highlights interferon (IFN)-related pathways and the brown asterisk MTOR-related pathways. G2M = Gap 2 phase mitosis; G-CSF = granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; NES = Normalized Enrichment Score; NFKB = nuclear factor κB; SCF = stem cell factor. STAT5 = signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; TNFA = tumor necrosis factor α; UV = ultraviolet.