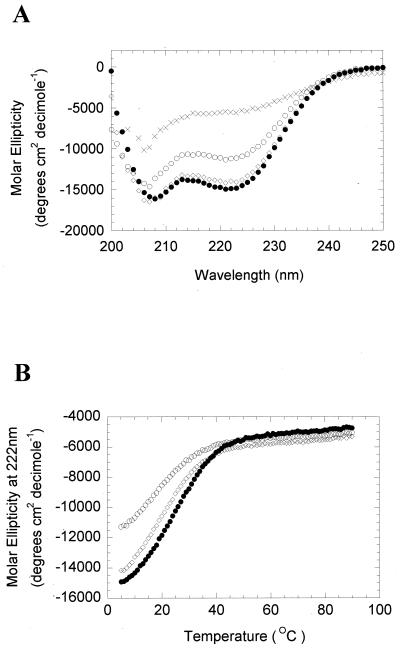
FIG. 3.
The BZLF1 peptides are α-helical in solution. (A) Three BZLF1 peptides pepB95-8…LLQHYREVAAAKSSENDRLRLLLKQMCPSLDV pepA205S…LLQHYREVASAKSSENDRLRLLLKQMCPSLDV pepA206S…LLQHYREVAASKSSENDRLRLLLKQMCPSLDV were synthesized on an Applied Biosystems 432A automated, continuous-flow peptide synthesizer using solid-phase 9-fluorenylmethoxy carbonyl chemistry and purified by high-pressure liquid chromatography (as described previously [11]). The secondary structures were analyzed using CD spectroscopy using a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter fitted with a six-cell changer Peltier temperature controller. The buffer system contained 25 mM potassium phosphate, 100 mM sodium chloride, and 1 mM dithiothreitol. The data are shown for peptide concentrations of 100 μM measured at 5°C. pepB95-8 is shown as closed circles, pepA205S as open circles, and pepA206S as open diamonds. The spectrum for pepB95-8 at 95°C is shown as crosses. (B) The signal of each BZLF1 peptide at 222 nm was determined using CD spectroscopy across the indicated range of temperatures. pepB95-8 is shown as closed circles, pepA205S as open circles, and pepA206S as open diamonds.