Figure 6. Reversed phase (C18) UPLC-HRMS analysis of Baeyer-Villiger intermediate.
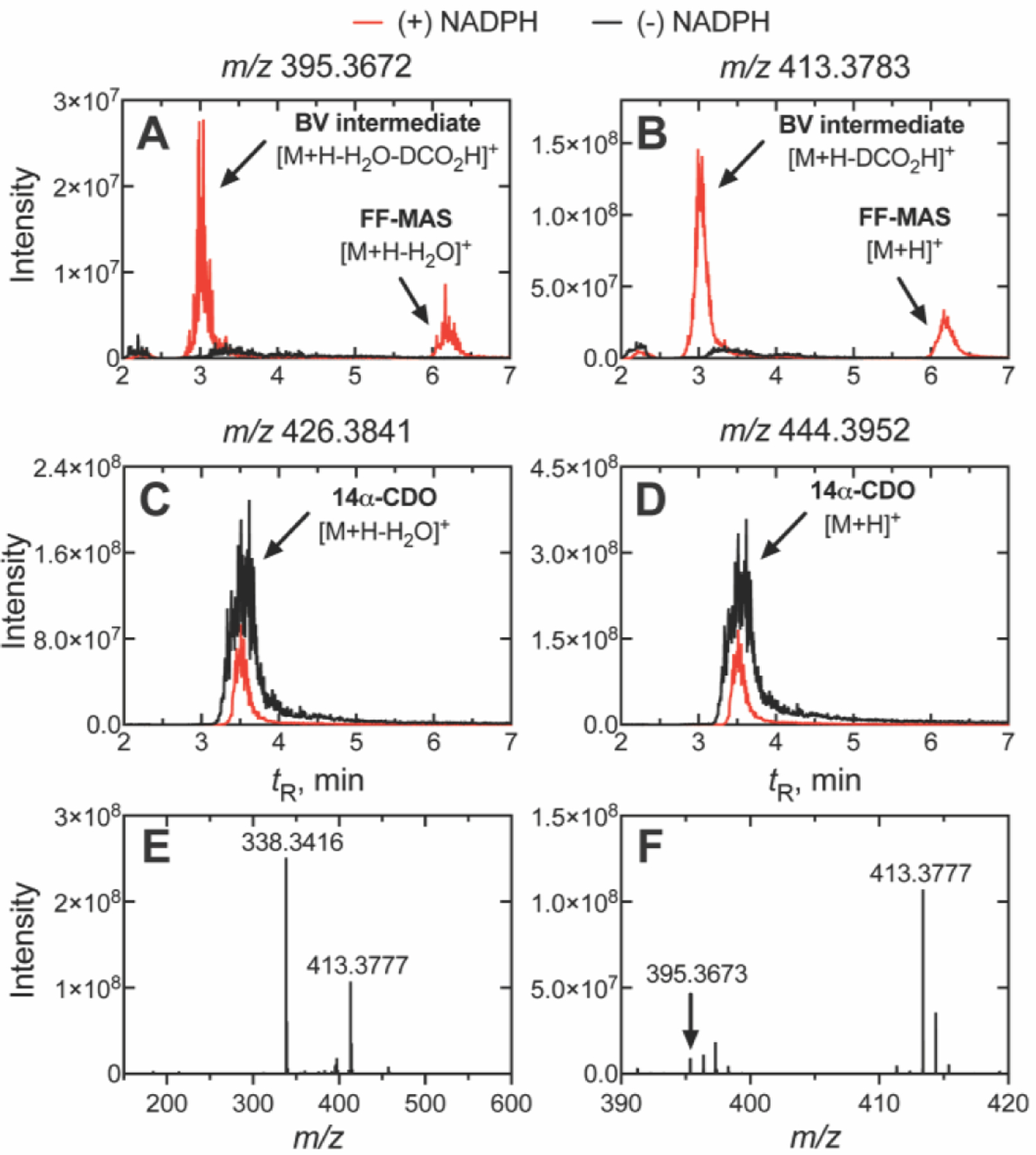
Steady-state incubations of P450 51A1 and 14α-CDO dihydrolanosterol were run for 2.5 min and the products were extracted and analyzed via (reversed phase) LC-ESI-HRMS. The extracted m/z values of (A) 395.3672 and (B) 413.3783 (utilizing a ± 5 ppm mass window) are fragment ions of the suspected Baeyer-Villiger (BV) intermediate corresponding to the [M+H-H2O-DCO2-H]+ and [M+H-DCO2-H]+ ions, respectively. Depletion of the aldehyde starting substrate (14α-CDO dihydrolanosterol) was observed with extracted m/z values of (C) 426.3841 and (D) 444.3952 corresponding to the intact [M+H]+ and [M+H-H2O]+ ions. The full mass spectrum (m/z 150–600) of the intermediate (tR 3.05 min, Panels A and B) showed the major [M+H- DCO2-H]+ fragment ion (m/z 413.3777) of the intermediate (Panel E), while the minor [M+H-H2O- DCO2-H]+ fragment ion (m/z 395.3673) was observable when the trace was magnified (m/z 390–420, Panel F). The Baeyer-Villiger (BV) intermediate (tR 3.05 min) eluted as an early shoulder of the substrate peak (14α-CDO dihydrolanosterol, tR 3.51 min) while FF-MAS eluted later (tR 6.17 min). similar to the results reported by Fischer et al.[12c] (The corresponding raw chromatographic traces are presented in Figure S8). (The ion m/z 338.3416 in Panel E is from a closely eluting peak (ΔtR 0.1 min) and could not be identified; it is not a fragment of m/z 413.3777).
