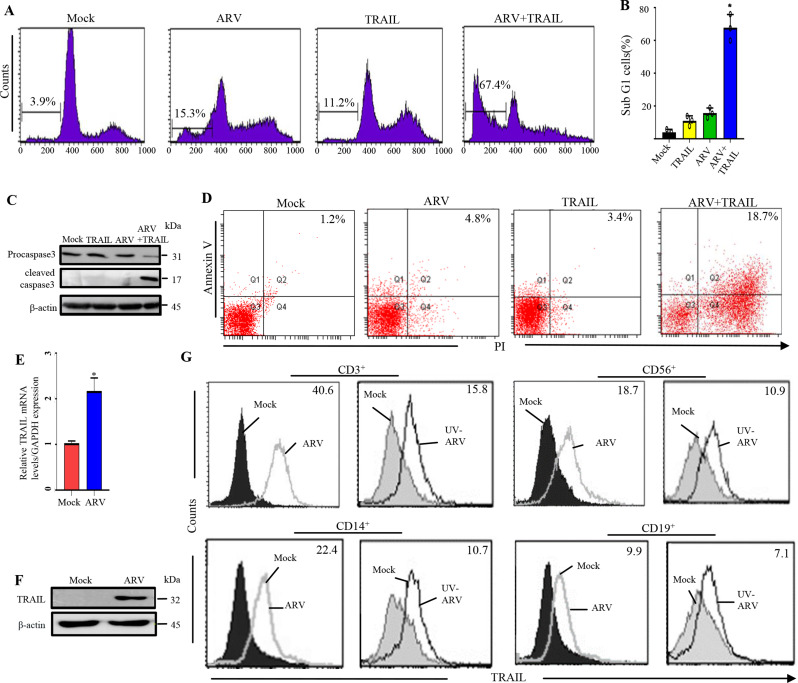
Fig. 1.
ARV-induced apoptosis in AGS cells through the TRAIL signaling pathway and ARV-induced expression of TRAIL on PBMCs driven by IFN-γ sensitization. (A) AGS cells were infected with ARV at an MOI of 10 for 24 h and sensitized in the presence or absence of recombinant TRAIL protein (25 ng/mL). Sub-G1 cell populations were analyzed by flow cytometry. Counts: the number of events (cell count) on the y-axis. (B) Graph shown represents the mean ± SE calculated from three independent experiments. *p < 0. 05 * * p < 0.01. In this work, the statistical methods of Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 are the same as the Fig. 1. (C) AGS cells were infected with ARV at an MOI of 10 for 24 h and sensitized in the presence or absence of recombinant TRAIL protein (25 ng/mL). Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot assays. All original/uncropped blots and images from this study are provided in supplementary Fig. 7. (D) To detect cell death, annexin V and PI double staining was used in flow cytofluorimetric analyses. The data generated by flow cytometry are plotted in two-dimensional dot plots in which PI is represented versus annexin V-FITC. Apoptotic cells which are PI and Annexin positive (PI/FITC +/+). PBMCs were sensitized with ARV at an MOI of 10. TRAIL levels were analyzed 24 h post-sensitization. PBMCs were isolated from normal healthy volunteers (n = 3). Similar results were observed in 3 different PBMC samples. The expression levels of TRAIL were examined by qRT-PCR (E) Western blot assays (F). (G) TRAIL expression on human PBMC after ARV or UV-ARV sensitization. The expression levels of TRAIL were analyzed by 24 h later on CD3+, CD14+, CD19+, and CD56+ cells using two-color flow cytometry. Representative results are shown in histograms based on 104 gated cells in all conditions, relative mean fluorescence intensity (RMFI) is shown on histograms. Cell viability was > 95%, as assessed by PI exclusion. Similar results were observed using at least 3 different PBMC donors