FIGURE 2.
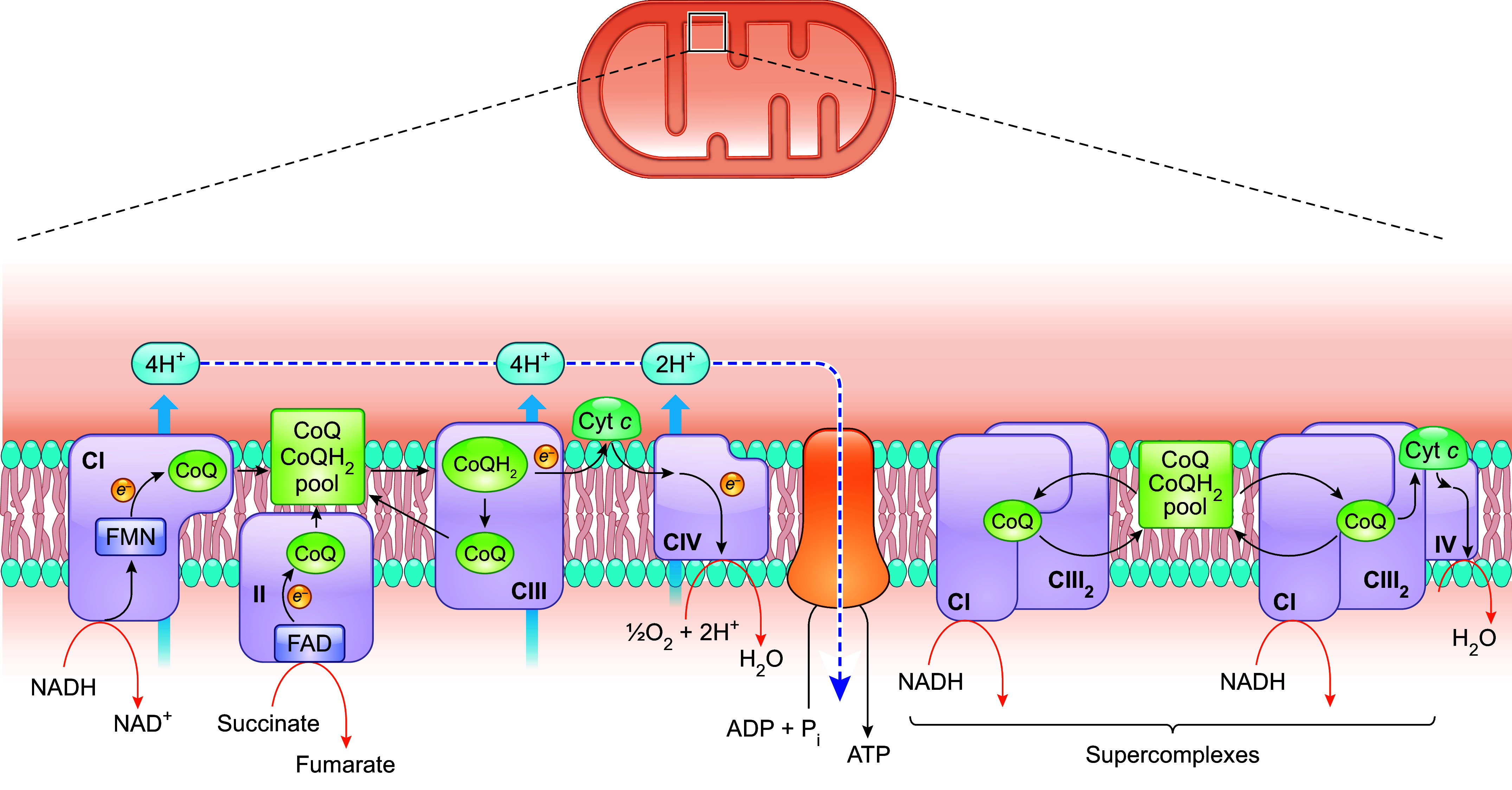
Functions of CoQ in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. CoQ is a pivotal component of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, acting as a mobile electron carrier shuttling electrons from CI and CII to CIII. During this process, CoQ cycles between reduced and oxidized states. In addition to moving randomly and colliding with CI and CII, CoQ is also present in CI- and CIII-containing respiratory supercomplexes (SCs), formed by the dynamic association of ETC complexes. In SCs, CIII is normally observed as a dimer (CIII2). All CoQ in the IMM likely behaves as a single functional pool, that is, CoQH2 can diffuse out of the CI and CIII assembled in SCs and become oxidized by CIII found outside of SCs. Conversely, CoQH2 generated independently of SCs can diffuse in, and be oxidized by, CIII attached to CI assembled in SCs. See glossary for other abbreviations.
