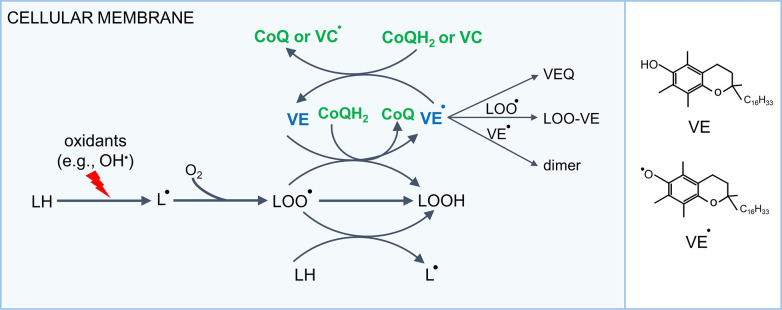
FIGURE 11.
Antioxidant action of vitamin E (VE) against lipid peroxidation. VE scavenges lipid peroxyl radical (LOO•) before it attacks other lipids (LH) to form lipid hydroperoxide (LOOH) and a new lipid radical (L•), by which it terminates lipid peroxidation chain reactions. This leaves behind the vitamin E radical (VE•). VE• can be converted back to the reduced antioxidant form by CoQ or vitamin C (VC). VE• can also react with another LOO•, forming poorly reactive nonradical adducts, decay by reaction with another VE• molecule to give inactive dimers, or be completely oxidized to vitamin E quinone (VEQ). VC•, vitamin C radical. See glossary for other abbreviations.