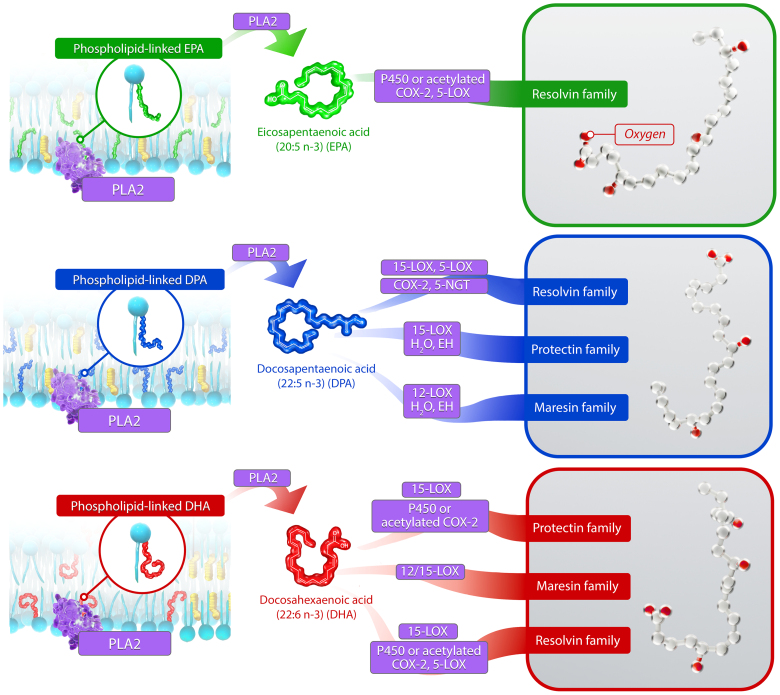
Figure 1.
Multiple enzymes, including COXs (cyclooxygenases), LOXs (lipoxygenases), and CYP (cytochrome P450), generate pro-resolving oxylipins from omega-3 fatty acid (n3-FA) precursors. The n3-FAs concentrate in cell membranes and are then released enzymatically by PLA2 (phospholipase A2) before conversion to pro-resolving oxylipins by P450, 12/15-LOX, and COX2 (including acetylated COX2). The structures of representative oxylipins from each n3-FA are shown in the boxes on the right, where the oxygen atoms are highlighted red. 5-NGT indicates 5-nitrosoglutathione; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DPA, docosapentaenoic acid; EH, epoxide hydrolase; and EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid.