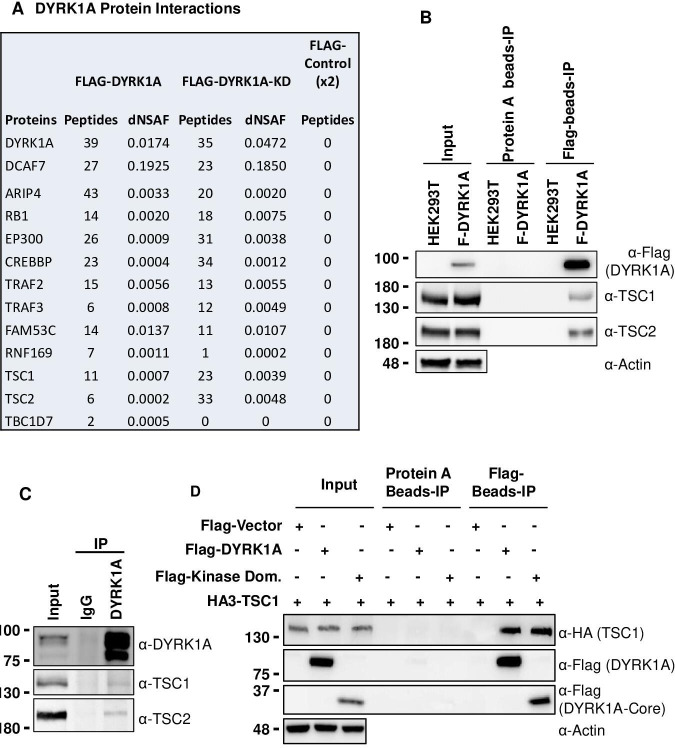
Figure 2. Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) interacts with the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC).
(A) The tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) datasets previously acquired by MudPIT analyses of FLAG-DYRK1A affinity purifications and negative FLAG controls (Li et al., 2018) were searched against the most recent releases of the human protein sequence databases (built by collating and removing redundant entries from NCBI Homo sapiens RefSeq GCF_000001405.40_GRCh38.p14 and GCF_009914755.1_T2T-CHM13v2.0). Highly enriched proteins include known and novel DYRK1A-interacting partners and are reported with their peptide counts and distributed normalized spectral abundance factor (dNSAF) values, which reflect their relative abundance in the samples (Zhang et al., 2010). (B) Flag beads were used to pull down Flag-DYRK1A from whole cell extracts of HEK293 transfected with Flag-DYRK1A, and Protein A beads were used as a control. The blots were probed with TSC1 and TSC2 antibodies. Actin was used to normalize the lysate inputs. (C) Endogenous DYRK1A was immunoprecipitated with DYRK1A antibody from HEK293 cytoplasmic fraction generated using the Dignam protocol (Li et al., 2018) and probed with antibodies against endogenous DYRK1A, TSC1, and TSC2. Rabbit IgG was used as the IP control (D) Flag-DYRK1A and Flag-DYRK1A kinase domain constructs were affinity purified using Flag-beads from HEK293 cells co-transfected with HA3-TSC1 and probed with α-HA and α-Flag antibodies. Actin was used as the loading control.
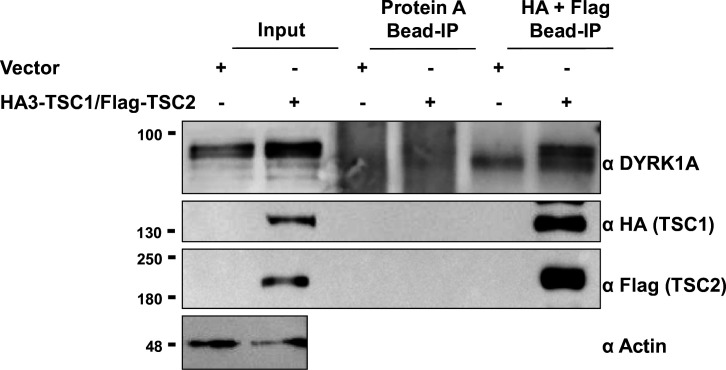
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. TSC1/TSC2 interact with dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A).
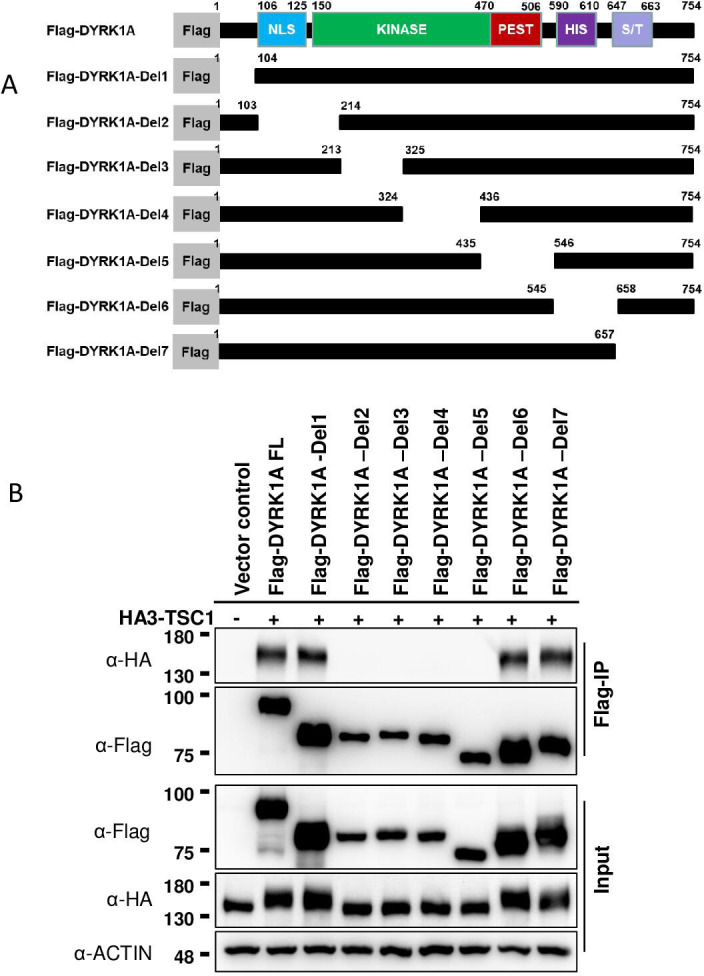
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) kinase domain interacts with TSC1.