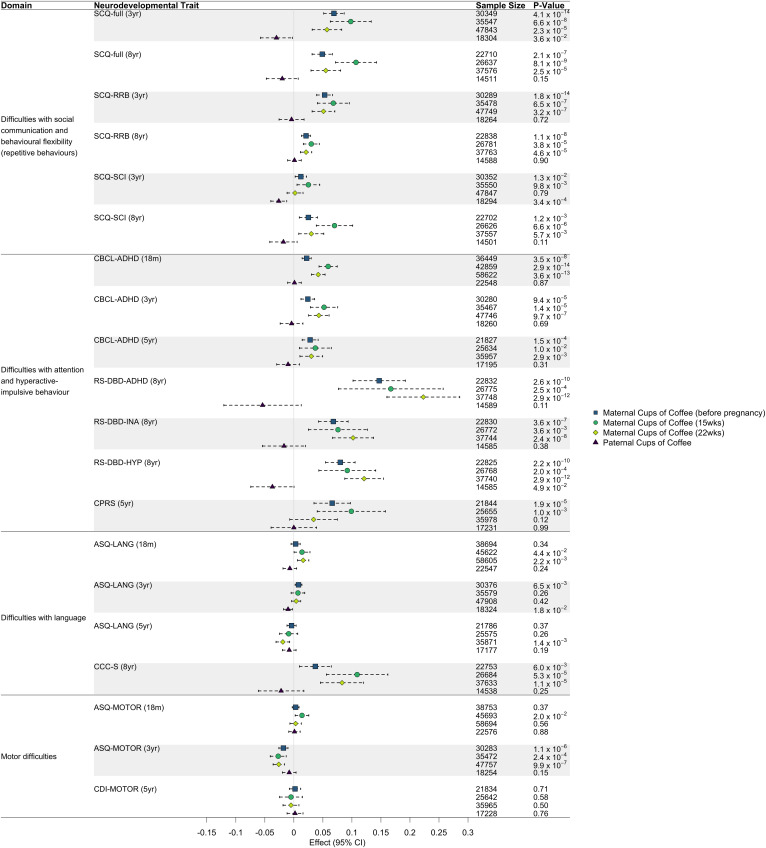
Figure 1.
Effect estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) from the traditional observational analyses assessing the relationship between both maternal and paternal coffee consumption exposure (cups/day) and offspring neurodevelopmental difficulties (ND) outcomes (rank-based inverse normal transformed) using linear regression. Covariates included offspring birth year, maternal age at birth and paternal age at birth. SCQ-full, Social Communication Questionnaire; SCQ-RRB, Social Communication Questionnaire restricted and repetitive behavior subscale; SCQ-SCI: Social Communication Questionnaire social communication impairment subscale; CBCL-ADHD: Child Behavior Checklist ADHD subscale; RS-DBD-ADHD: Rating Scale for Disruptive Behavior Disorders ADHD subscale; RS-DBD-INA: Rating Scale for Disruptive Behavior Disorders inattention subscale; RS-DBD-HYP: Rating Scale for Disruptive Behavior Disorders hyperactivity subscale; CPRS, Conners Parent Rating Scale-Revised short form; ASQ-LANG: Ages and Stages Questionnaire language subscale; CCC-S: The Children's Communication Checklist-2 Short Scale; ASQ-MOTOR: Ages and Stages Questionnaire motor items; CDI-MOTOR: Child Development Inventory motor subscale.