Abstract
Clones expressing renal dipeptidase (EC 3.4.13.11) have been isolated from a pig kidney cortex cDNA library after employing the polymerase chain reaction technique to amplify a region of the dipeptidase cDNA. The complete primary sequence of the enzyme has been deduced from a full length cDNA clone. This predicts a protein of 409 amino acids, a cleavable N-terminal signal sequence of 16 residues and two N-linked glycosylation sites. At the C-terminus of the predicted sequence is a stretch of mainly hydrophobic amino acids which is presumed to direct the attachment of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Expression of the mRNA for pig renal dipeptidase in Xenopus laevis oocytes led to the production of a disulphide-linked dimeric protein of subunit Mr 48,600 which was recognized by a polyclonal antiserum raised to renal dipeptidase purified from pig kidney cortex. Bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C released renal dipeptidase from the surface of the oocytes and converted the amphipathic detergent-solubilized form of the dipeptidase to a hydrophilic form, indicating that Xenopus laevis oocytes can process expressed proteins to their glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchored form.
Full text
PDF


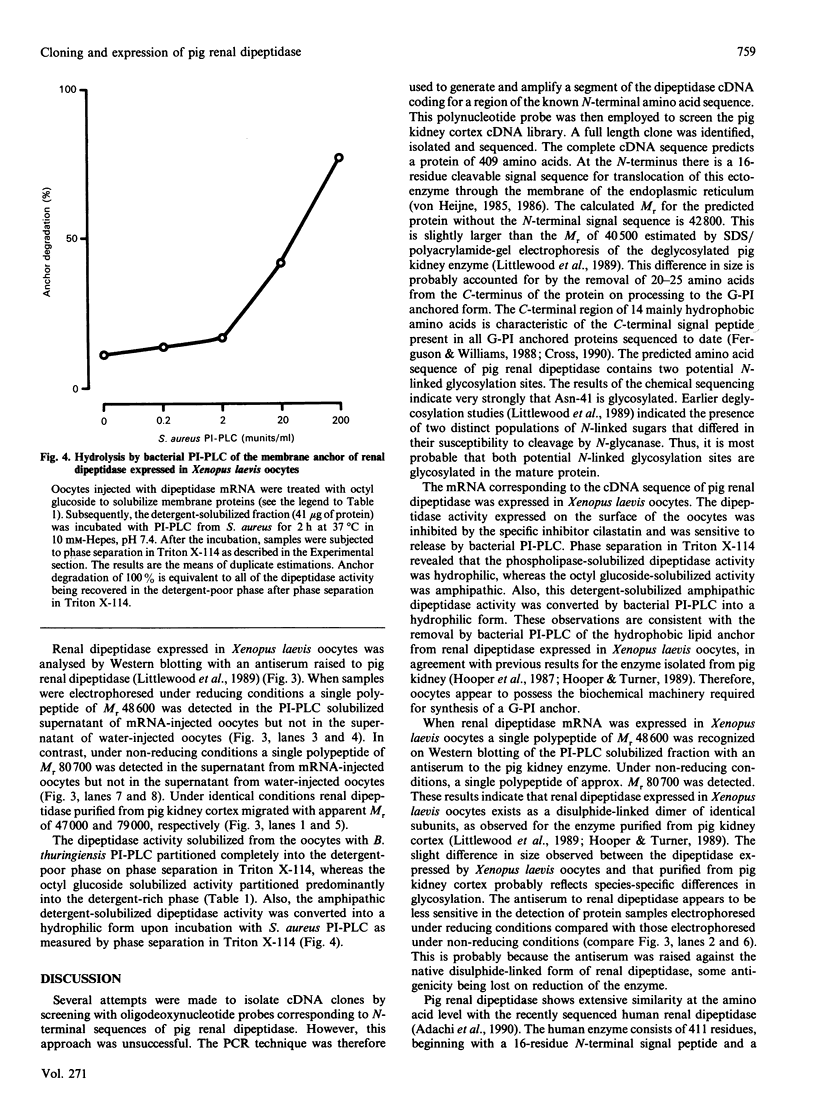

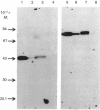
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi H., Tawaragi Y., Inuzuka C., Kubota I., Tsujimoto M., Nishihara T., Nakazato H. Primary structure of human microsomal dipeptidase deduced from molecular cloning. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3992–3995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. J., Mukhopadhyay S. K., Campbell B. J. Physicochemical characterization of renal dipeptidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1745–1750. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Hryszko J., Turner A. J. Purification and characterization of pig kidney aminopeptidase P. A glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored ectoenzyme. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):509–515. doi: 10.1042/bj2670509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Keen J. N., Turner A. J. Characterization of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored human renal dipeptidase reveals that it is more extensively glycosylated than the pig enzyme. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):429–433. doi: 10.1042/bj2650429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Differential solubilization by detergents can predict a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2500865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Isolation and characterization of the amphipathic form of renal dipeptidase and hydrolysis of its glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor by an activity in plasma. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2610811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Isolation of two differentially glycosylated forms of peptidyl-dipeptidase A (angiotensin converting enzyme) from pig brain: a re-evaluation of their role in neuropeptide metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2410625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Bouvier J., Bairoch A. A unique signature identifies a family of zinc-dependent metallopeptidases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak E. M., Tate S. S. Glutathione-degrading enzymes of microvillus membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6322–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Hajdu R., Kahan F. M. Metabolism of thienamycin and related carbapenem antibiotics by the renal dipeptidase, dehydropeptidase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Wu X. W., Gibbs R. A., Cook R. G., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Generation of cDNA probes directed by amino acid sequence: cloning of urate oxidase. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.3344434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood G. M., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Affinity purification, characterization and localization of the phospholipase C-solubilized form of renal dipeptidase. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2570361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Translation of messenger RNA in injected frog oocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:288–296. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.7302589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Auld D. S. Active-site zinc ligands and activated H2O of zinc enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]