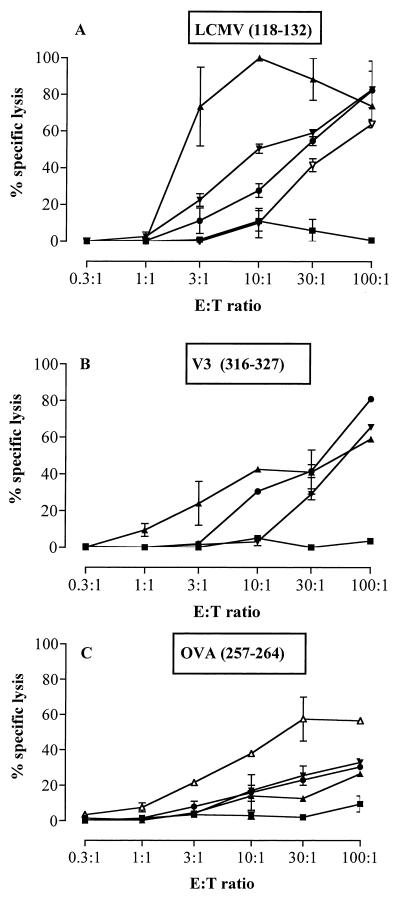
FIG. 4.
Immunization of mice with detoxified CyaA toxoids bearing multiple epitopes in the absence of adjuvant induces high specific CTL responses. BALB/c (A and B) and C57BL/6 (C) mice (n = 3 for each group) were immunized i.p. on days 0 and 14 with 50 μg of CyaA toxoids carrying the polyepitope at different sites (108 [●], 233, [▴], or 336) [▾] or with either the LCMV (▿) or OVA (▵) epitope at site 224 or with control detoxified CyaA (CyaA wt-E5) (■) in PBS. Seven days later, animals were sacrificed, the splenocytes were restimulated in vitro for 5 days with 1 μg of the LCMV (A), V3 (B), or OVA (C) peptide per ml in the presence of irradiated syngeneic splenocytes and used as effectors against unsensitized target cells (P815 for panels A and B and EL4 for panel C) or against target cells sensitized with the same peptide as used for in vitro stimulation. Target lysis was evaluated by 51Cr release. Lysis of unsensitized target cells was less than 10% and is not shown. (A and B) LCMV (p118–132)-specific CTL (A) and V3 (p316–327)-specific CTL (B) responses in the same BALB/c mice injected with the detoxified recombinant CyaA toxoids. (C) OVA (p257–264)-specific CTL response in C57BL/6 mice injected with the detoxified recombinant CyaAs. CTL responses of control mice injected with the wild-type CyaA-E5 are shown to illustrate the specificity of the responses. The data represent the mean percentage of the specific lysis values from duplicate samples and standard error of the mean and are representative of two experiments. E:T ratio, effector-to-target-cell ratio.