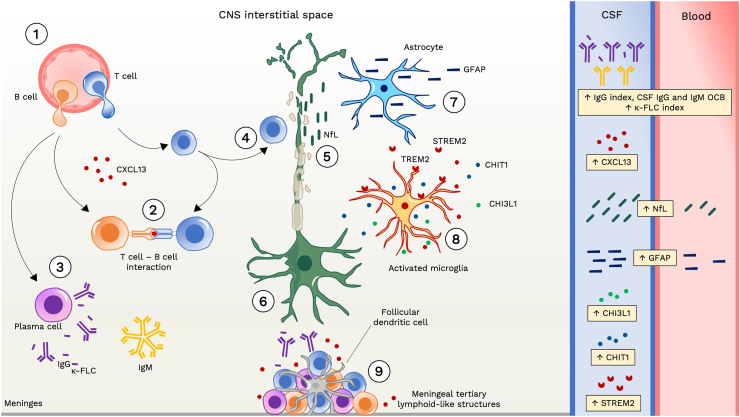
Fig. 2.
Pathophysiological basis of fluid biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. (1) In the early stages of the disease, immune cells infiltrate the central nervous system (CNS) through the blood–brain barrier. This includes macrophages, CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, B cells, and plasma cells. T and B cells are primed in the periphery and attracted to the CNS by chemotactic factors, like chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (CXCL13) for B cells. (2) Within the CNS, T cells and B cells interact closely, with B cells serving as antigen-presenting cells. (3) Activated B cells can mature into plasma cells, secreting IgG and IgM antibodies into the intrathecal space. This process also results in the release of free light chains (FLC) due to a mismatch between immunoglobulin light and heavy chains synthesis. (4–5) The inflammatory process leads to axonal damage, and the release of neuronal markers like neurofilament light chain (NfL) into the interstitial space, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and bloodstream. (6) Focal axonal injury induces axonal die-back or retrograde degeneration as well as Wallerian or anterograde degeneration contributing to neuronal loss. (7–8) CNS resident immune cells such as microglia and astrocytes become activated, impacting axon and synaptic integrity and function. Activated microglia and astrocytes release various mediators into the CSF, including soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (sTREM2), chitinase 1 (CHIT1) and chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1). Additionally, astrocytic injury results in the release of structural proteins like glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) into both the CSF and bloodstream. (9) Failure to resolve inflammation adequately over time leads to sustained immune response, resulting in persistent meningeal inflammation with formation of lymphoid structures. Abbreviations. CHI3L1: chitinase-3-like protein 1. CHIT1: chitinase 1. CNS: central nervous system. CSF: cerebrospinal fluid. CXCL13: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13. FLC: free light chain. GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein. NfL: neurofilament light chain. sTREM2: soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2. TREM2: cell surface triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.