FIGURE 1.
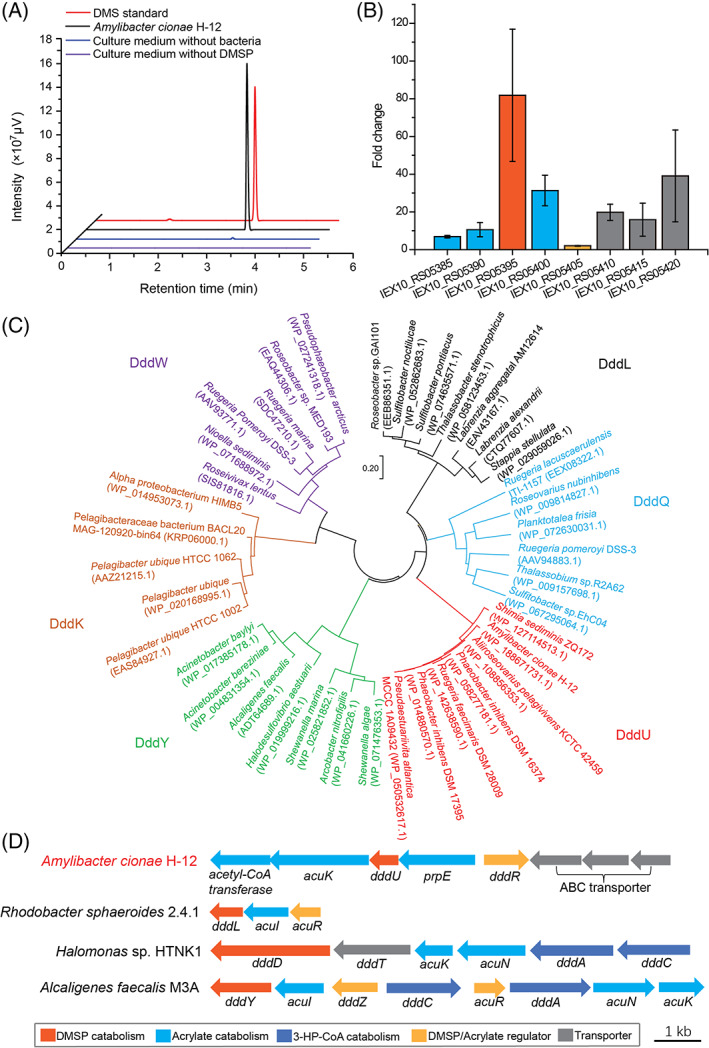
Analysis of Amylibacter cionae H‐12 dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) lyase activity and its candidate DMSP lyase. (A) Gas chromatography detection of DMSP‐dependent dimethyl sulphide (DMS) production by strain H‐12. The culture medium without bacteria and the medium without DMSP were used as the controls. The DMS standard was used as a positive control. (B) Transcriptomic analysis of putative DMSP/acrylate‐catabolizing genes from H‐12. The fold changes were calculated by dividing the gene transcripts in the presence of 5 mM DMSP by those in the absence of DMSP. The error bar represents standard deviation of triplicate experiments. (C) Neighbour‐joining phylogenetic tree of DddU and representative proteins of the five other reported cupin‐containing DMSP lyases. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA version 7.0 (Tamura et al., 2013). (D) Genetic organization of the putative DMSP‐catabolizing gene cluster in strain H‐12. DMSP catabolic genes and their regulators from Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1, Halomonas sp. HTNK1 and Alcaligenes faecalis M3A were shown (Curson, Sullivan, et al., 2011).
