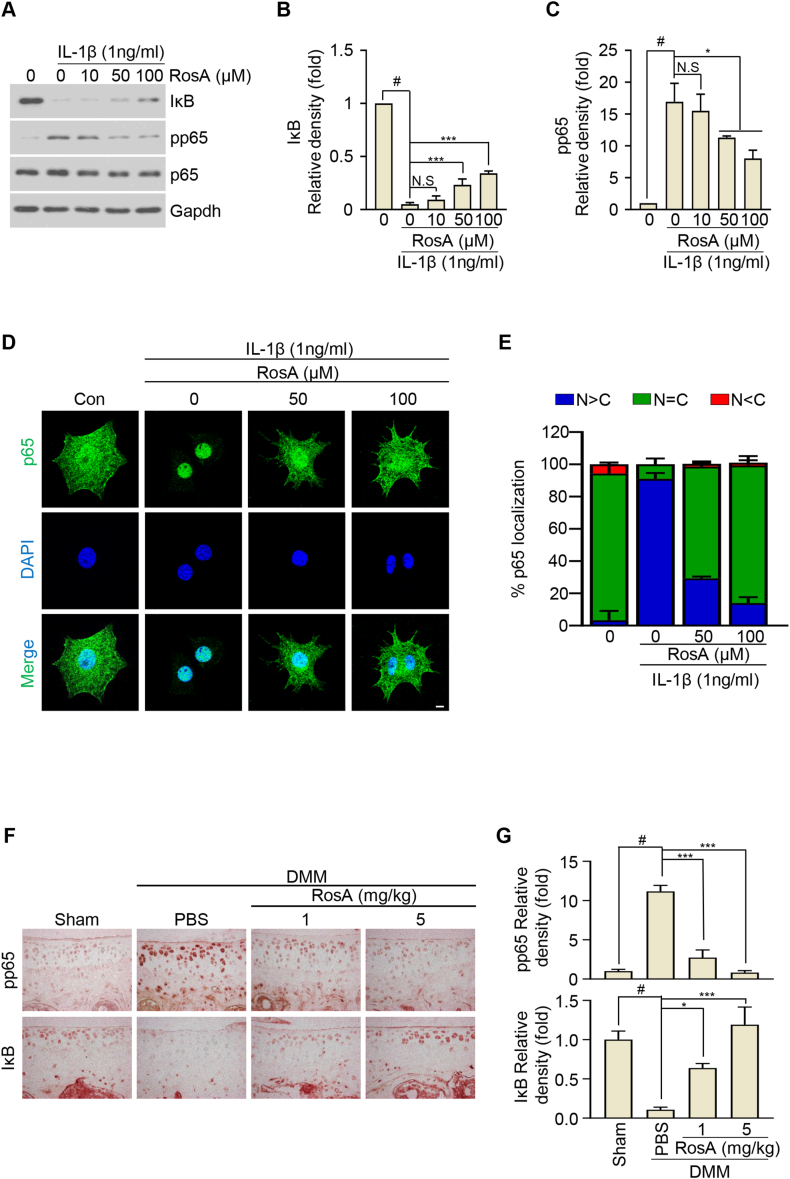
Fig. 4.
RosA suppresses the expression of catabolic factors via the NF-κB signaling pathway.
(A, B, C) Chondrocytes were exposed to RosA at the indicated concentration for 24 h before being treated to IL-1β (1 ng/ml) for 15 min. Western blot analysis was performed to evaluate the Phosphorylation of p65 and the degradation of IκB (A) and densitometry analysis (B; IκB, C; pp65). (D) Chondrocytes were subjected to immunofluorescence staining for p65 (green) and 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) was used for nuclear staining. (E) The nuclear (N)-cytoplasmic (C) ratio of p65 was analyzed in three randomly chosen regions from three separate experiments (n = 100 cells per field). Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) The pp65 and IκB protein levels in OA mice cartilage after i,a-injection of RosA assessed by Immunohistochemical staining and (G) quantification. Scale bars, 100 μm. Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. One-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni's test was used to determine significant differences. None significant (N.S), ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, #P < 0.05 compared to the control group. Original blots (Fig. S8) can be seen in supplementary figures file.