FIG. 2.
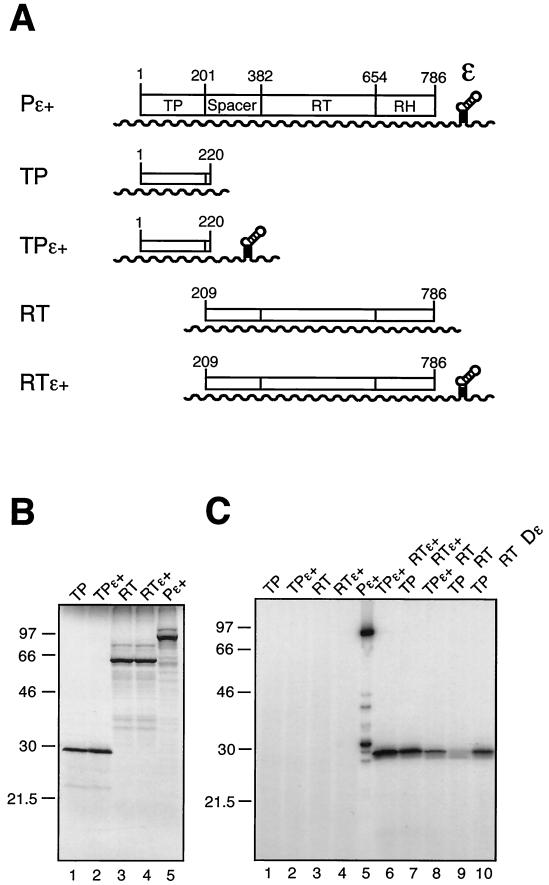
Functional trans-complementation of DHBV P protein domains coexpressed in RRL. (A) Schematic drawing of plasmid constructs and RNA transcripts used for in vitro translation. ORFs are given as boxes, and T7 promoter-driven transcripts are shown as wavy lines. Plasmid pT7AMVpol (Pɛ+) contains the complete 786-aa P protein ORF; the approximate borders of the four P protein domains are indicated by amino acid positions. Constructs Pɛ+, pT7-TP1-220ɛ+ (TPɛ+), and pT7-RT209-786ɛ+ (RTɛ+) carry a cis Dɛ element downstream of the coding region, whereas pT7-TP1-220 (TP) and pT7-RT209-786 (RT) are Dɛ deficient. (B) [35S]Met-labeled in vitro translation products of the constructs shown in panel A. Proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Molecular size markers are given in kilodaltons. (C) In vitro cotranslation and protein priming assay in the presence of [α-32P]dATP. Priming assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. In the sample shown in lane 10 a 76-nt Dɛ RNA in vitro transcript was supplied in trans at a 1 μM concentration. An equal volume of each sample (except for Pɛ+ [20%]) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The band of about 32 kDa in the Pɛ+ sample corresponds most likely to a degradation product of the 32P-primed full-length P protein and did not occur as prominently in similar experiments.