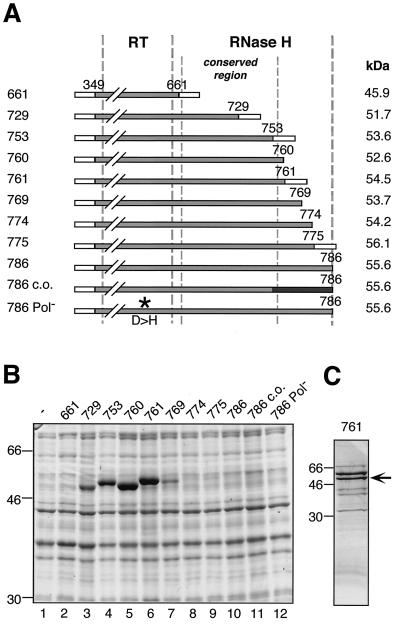
FIG. 6.
Bacterial expression and purification of the RT-RH domain. (A) Schematic drawing of C-terminally truncated RT-RH constructs analyzed for protein expression in E. coli. Each construct starts with 50 vector-derived aa (open boxes at left) followed by DHBV P sequence from aa 349 to the indicated C-terminal position. Some constructs contain short vector-encoded C-terminal tags (open boxes at right). Numbers on the left represent abbreviations of the construct names; e.g., “661” refers to plasmid pET-RT349-661. Construct pET-RT349-786 c.o. is codon optimized for E. coli in the C-terminal region (black box). Construct pET-RT349-786Pol− contains a D-to-H amino acid substitution in the YMDD motif of the polymerase active site (asterisk). Borders of the RT and RH domains are indicated by thick vertical broken lines. The conserved region of the RH domain from aa 660 to 759 (9) is labeled by thin broken lines. (B) Expression of RT-RH constructs in E. coli strain BL21-CodonPlus-RIL. Total cell lysates of induced bacterial cultures were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining; molecular mass markers are given in kilodaltons. (C) Purification of bacterially expressed RT349-761. The soluble fraction of RT349-761 was purified by IMAC and subsequent dialysis against a physiological buffer. The purified protein fraction was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The nominally 54-kDa RT349-761 protein is marked by an arrow. Additional bands of 60 kDa (strong) and 70 kDa (weak) were identified by immunoblotting as E. coli GroEL and DnaK.