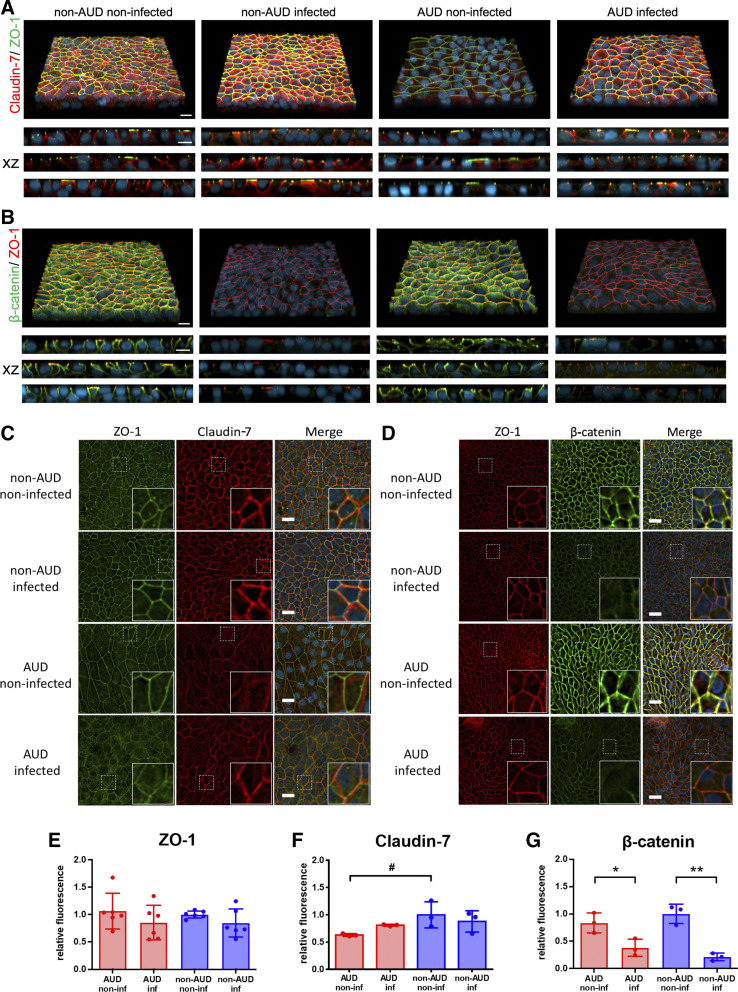
Figure 5.
Changes to non-alcohol use disorder (AUD) and AUD bronchial cell junctions in response to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. A–D: cells 72 h postinfection or mock infection were fixed and immunostained for zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1, green) and claudin-7 (red) and DAPI (blue) (A and C) or ZO-1 (red), β-catenin (green), and DAPI (blue) (B and D) and imaged by confocal (A and B) and deconvolution (C and D) fluorescence microscopy. A and B: top panels show a three-dimensional (3-D) projection, the bottom panels represent xz projections from three biological replicates for each condition. Bar, 10 μm. C and D: xy projections of representative images. White dotted squares represent the location of insets in the bottom right corner of each image. Bar, 20 micron. E–G: SARS-CoV-2 infection had little effect on relative fluorescence intensity of ZO-1 (E) and claudin-7 (F), however there was a significant decrease in total β-catenin (G) 72 h postinfection (*P = 0.027, **P = 0.001, n = 3 biological replicates consisting of 3 image fields each). Also, there was a trend towards less claudin-7 in noninfected AUD cells compared with noninfected non-AUD cells (#P = 0.076, n = 3 biological replicates consisting of 3 image fields each), although this difference diminished 72 h postinfection. Values represent means ± SD in each case. Samples were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test.