Abstract
The sequence of squid (Loligo forbesi) rhodopsin was determined by protein and cDNA sequencing. The protein has close similarity to octopus rhodopsin, having an N-terminal region (residues 1-340) which resembles other guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein)-linked receptors and a repetitive proline-rich C-terminus (residues 340-452). Comparison of the sequence of squid rhodopsin with those of other members of the G-protein-linked receptor superfamily reveals features which we predict to have both structural and functional importance.
Full text
PDF
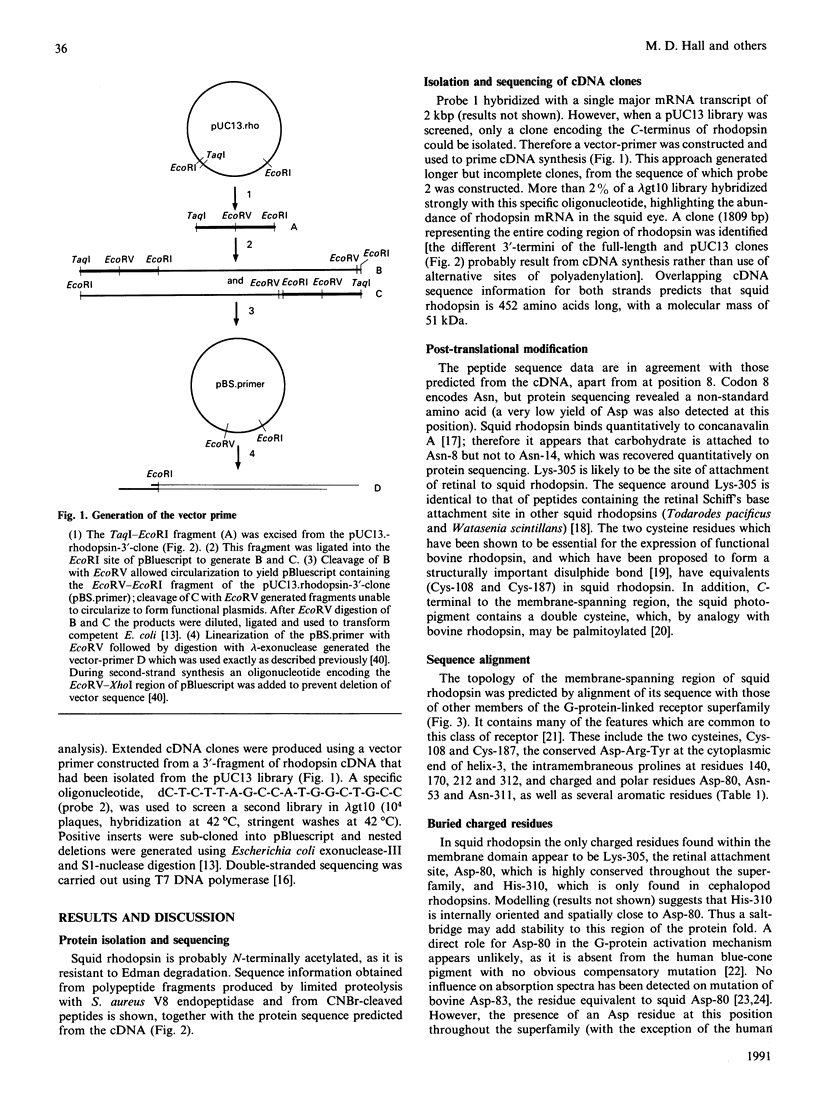


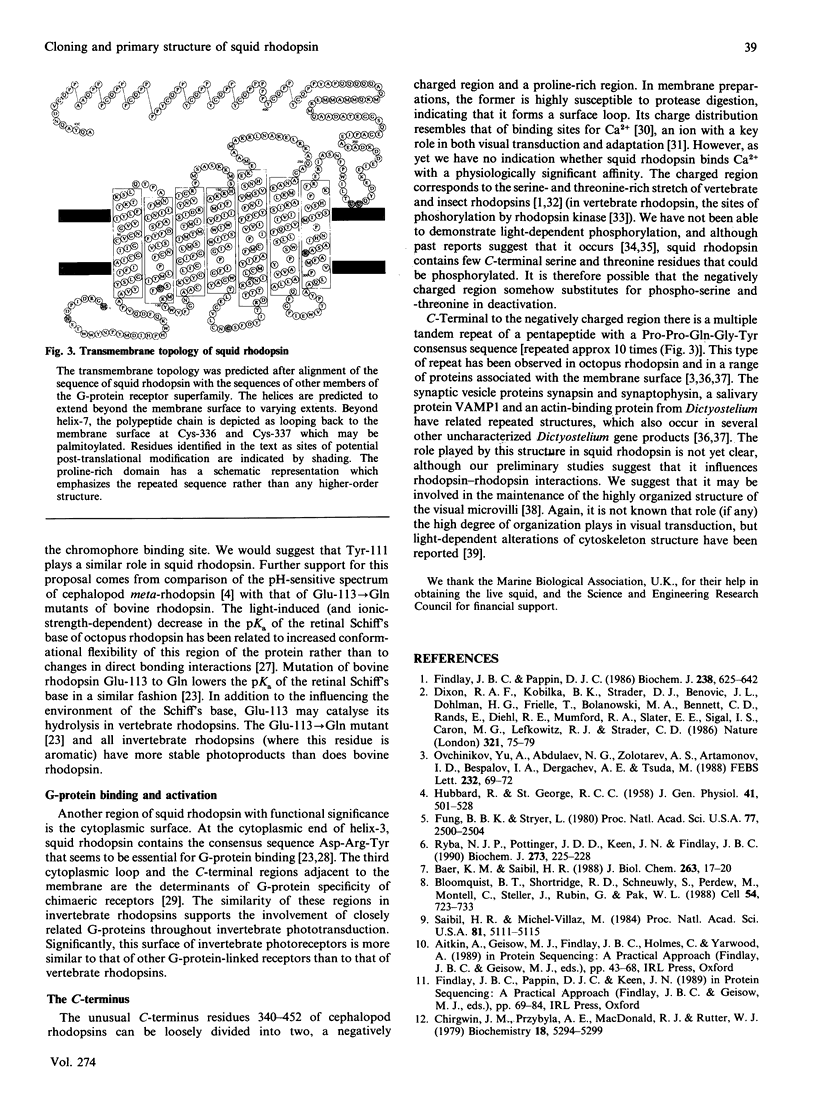

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer K. M., Saibil H. R. Light- and GTP-activated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in squid photoreceptor membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirala S. S., Kasturi R., Pazirandeh M., Stolow D. T., Huang W. Y., Wakil S. J. A novel cDNA extension procedure. Isolation of chicken fatty acid synthase cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3750–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B., Brett M., Pappin D. J. Primary structure of C-terminal functional sites in ovine rhodopsin. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):314–317. doi: 10.1038/293314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B., Pappin D. J. The opsin family of proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):625–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2380625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., König B., Sakmar T. P., Khorana H. G., Hofmann K. P. Rhodopsin mutants that bind but fail to activate transducin. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):123–125. doi: 10.1126/science.2218504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD R., ST GEORGE R. C. The rhodopsin system of the squid. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jan 20;41(3):501–528. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. J., De Caluwé G. L., De Grip W. J. Asp83, Glu113 and Glu134 are not specifically involved in Schiff base protonation or wavelength regulation in bovine rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 15;260(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutalos Y., Ebrey T. G., Gilson H. R., Honig B. Octopus photoreceptor membranes. Surface charge density and pK of the Schiff base of the pigments. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):493–501. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82394-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutalos Y., Ebrey T. G., Tsuda M., Odashima K., Lien T., Park M. H., Shimizu N., Derguini F., Nakanishi K., Gilson H. R. Regeneration of bovine and octopus opsins in situ with natural and artificial retinals. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2732–2739. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok-Keung Fung B., Stryer L. Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for bound GDP in retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashima K., Mitsudo M., Kito Y. Studies on cephalopod rhodopsin. Fatty acid esters of sucrose as effective detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Gerisch G., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. A protein with homology to the C-terminal repeat sequence of Octopus rhodopsin and synaptophysin is a member of a multigene family in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81521-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Zolotarev A. S., Artamonov I. D., Bespalov I. A., Dergachev A. E., Tsuda M. Octopus rhodopsin. Amino acid sequence deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen R., Hoppe I. Light-activated phosphorylation of cephalopod rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R., Corson D. W., Fein A. Pressure injection of calcium both excites and adapts Limulus ventral photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jul;88(1):107–126. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryba N. J., Pottinger J. D., Keen J. N., Findlay J. B. Sequence of the beta-subunit of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-directed GTP-binding protein from squid (Loligo forbesi) photoreceptors. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):225–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2730225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saibil H. R., Michel-Villaz M. Squid rhodopsin and GTP-binding protein crossreact with vertebrate photoreceptor enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saibil H., Hewat E. Ordered transmembrane and extracellular structure in squid photoreceptor microvilli. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):19–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. Glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8309–8313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidou M., Kubota I., Hiraki K., Kito Y. Amino acid sequence of the retinal binding site of squid visual pigment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 23;957(2):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Moffat K. The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8761–8777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Molecular biology of synaptic vesicle-associated proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):241–242. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Tsukita S., Matsumoto G. Light-induced structural changes of cytoskeleton in squid photoreceptor microvilli detected by rapid-freeze method. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1151–1160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A., Montal M. Light-regulated biochemical events in invertebrate photoreceptors. 2. Light-regulated phosphorylation of rhodopsin and phosphoinositides in squid photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2347–2352. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Effect of carboxylic acid side chains on the absorption maximum of visual pigments. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):928–930. doi: 10.1126/science.2573154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


