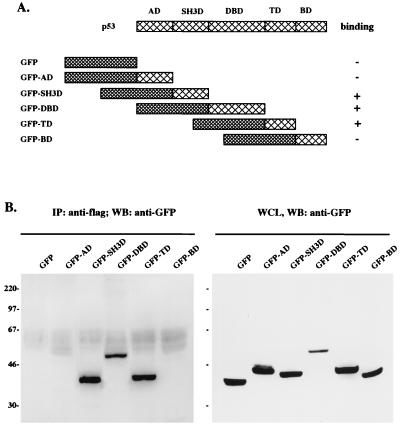
FIG. 4.
Mutational analysis of p53 for vIRF interaction. (A) Summary of p53 mutants. Individual domains of p53 were cloned in frame into the GFP vector to generate GFP-p53 fusion proteins. Boxes with large cross lines indicate individual domains of p53; boxes with small cross lines indicate GFP. AD, activation domain; SH3D, SH3B domain; DBD, DNA binding domain; TD, tetramerization domain; BD, basic domain. + and − indicate positive and negative binding of GFP-p53 fusion proteins to vIRF. (B) Identification of the vIRF binding domains of p53. 293T cells were cotransfected with Flag-tagged wt vIRF and GFP-p53 fusion constructs. Cell lysates were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-Flag antibody, followed by Western blotting (WB) with an anti-GFP antibody to detect GFP-p53 fusion proteins (left). Western blotting of whole-cell lysates with an anti-GFP antibody showed GFP-p53 expression in transfected 293T cells (right). Sizes are indicated in kilodaltons.