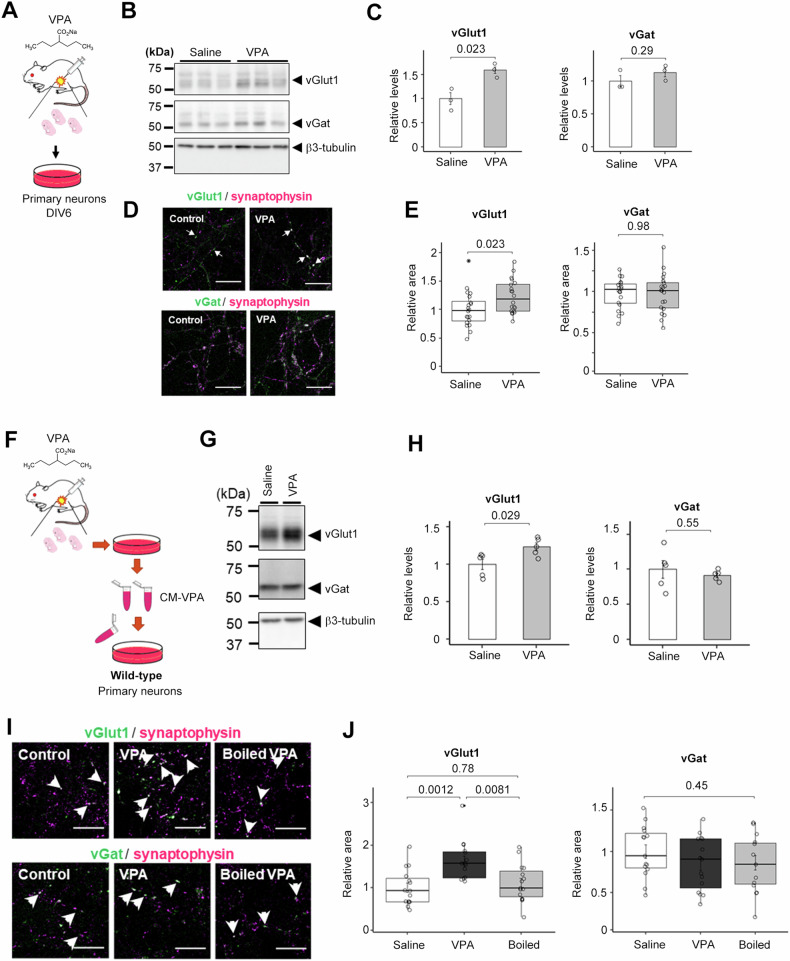
Fig. 1. Maternaly VPA-treated neurons secrete excitatory synapse-inducing factor(s).
A Schematic depiction of this experiment. 600 mg/kg VPA or saline was injected by i.p. into the pregnant mouse. B Immunoblot analysis of relative expression levels of synaptic proteins in mouse primary neurons obtained from maternal VPA-treated pups. C Quantification of the relative expression levels of synaptic proteins in B) (n = 3-4, Mean ± SEM, by Student’s t-test, n.s. indicates P > 0.05). Saline, saline-treated neuron; VPA, VPA-treated neuron’s medium. The expression of the vGlut1 was significantly increased, but the expression of the vGat was unchanged. D Immunocytochemical analyses of maternal VPA-treated primary neurons stained for synaptophysin, vGat, and vGlut1. Scale bar = 10 μm. E Quantification of vGlut1- and vGat-positive presynapse areas in D (n = 20, Mean ± SEM, by Student’s t-test, n.s. indicates P > 0.05). The area of vGlut1 positive puncta increased significantly, while the area of vGat positive puncta did not change. F Schematic depiction of this experiment. G Immunoblot analysis of synaptic protein levels in wild-type primary neurons treated with the conditioned medium of maternal VPA-treated neurons. Saline, Saline-treated neuron; VPA, VPA-treated neuron’s medium. H Immunoblot quantification of synaptic protein levels in B) (n = 5, Mean ± SEM, Student’s t-test, standardized by β3-tubulin). I Immunocytochemical analysis of vGlut1-, vGat-, and synaptophysin in wild-type primary neurons treated with the conditioned medium. Scale bar = 10 µm. J) Quantification of vGlut1- and vGat- positive presynapse areas in I (n = 15, MEAN ± SEM, One-way ANOVA was performed to assess the overall differences among groups. Post-hoc comparisons were conducted using Tukey’s Honest Significant Differences (HST) test, standardized by synaptophysin).