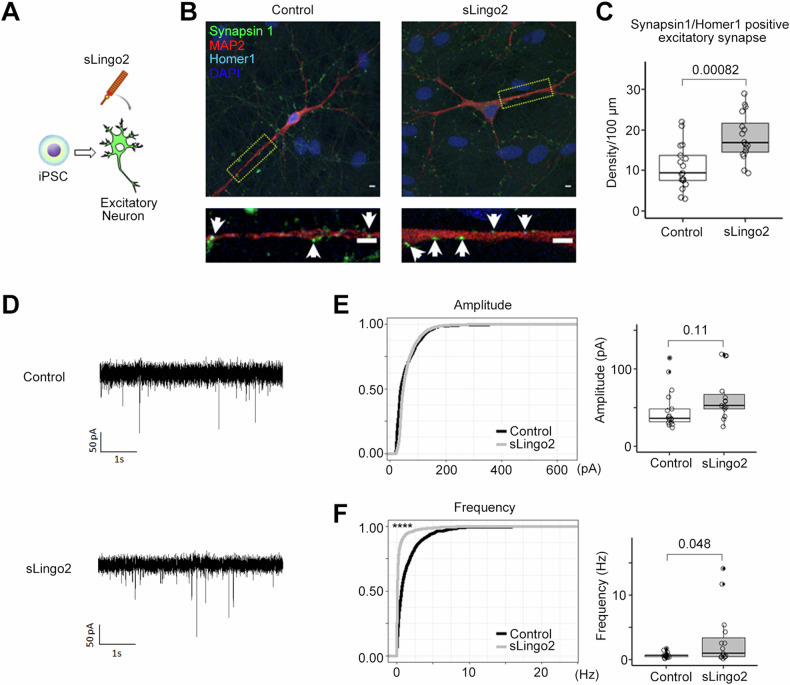
Fig. 6. Recombinant sLingo2 induces the excitatory synapse in human iPSC-derived neurons.
A Schematic depiction of this experiment. B Immunocytochemical analysis in sLingo2 treated induced Excitatory neuron. Green: synapsin1, Red: Map2, Blue: DAPI, Cyan: Homer1, Scale bar = 10 µm C Quantification of synapsin1, homer1 double-positive puncta number in (D) (n = 16–17, Mean ± SEM, Student’s t-test.). The double positive puncta number was increased with the administration of the sLingo2. D Representative mEPSC recordings from sLingo2 treated iPSC-derived excitatory neurons. E Cumulative probability of mEPSC amplitude and frequency. F Quantification of average mEPSC amplitude and frequency (n = 15, 17. Mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test for average. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test for frequency. ****p < 0.0001). The average mEPSC frequency was increased with the administration of the sLingo2, while amplitude did not.