Fig. 1. isoTOP-ABPP identifies privileged, formaldehyde-sensitive cysteine sites across the proteome.
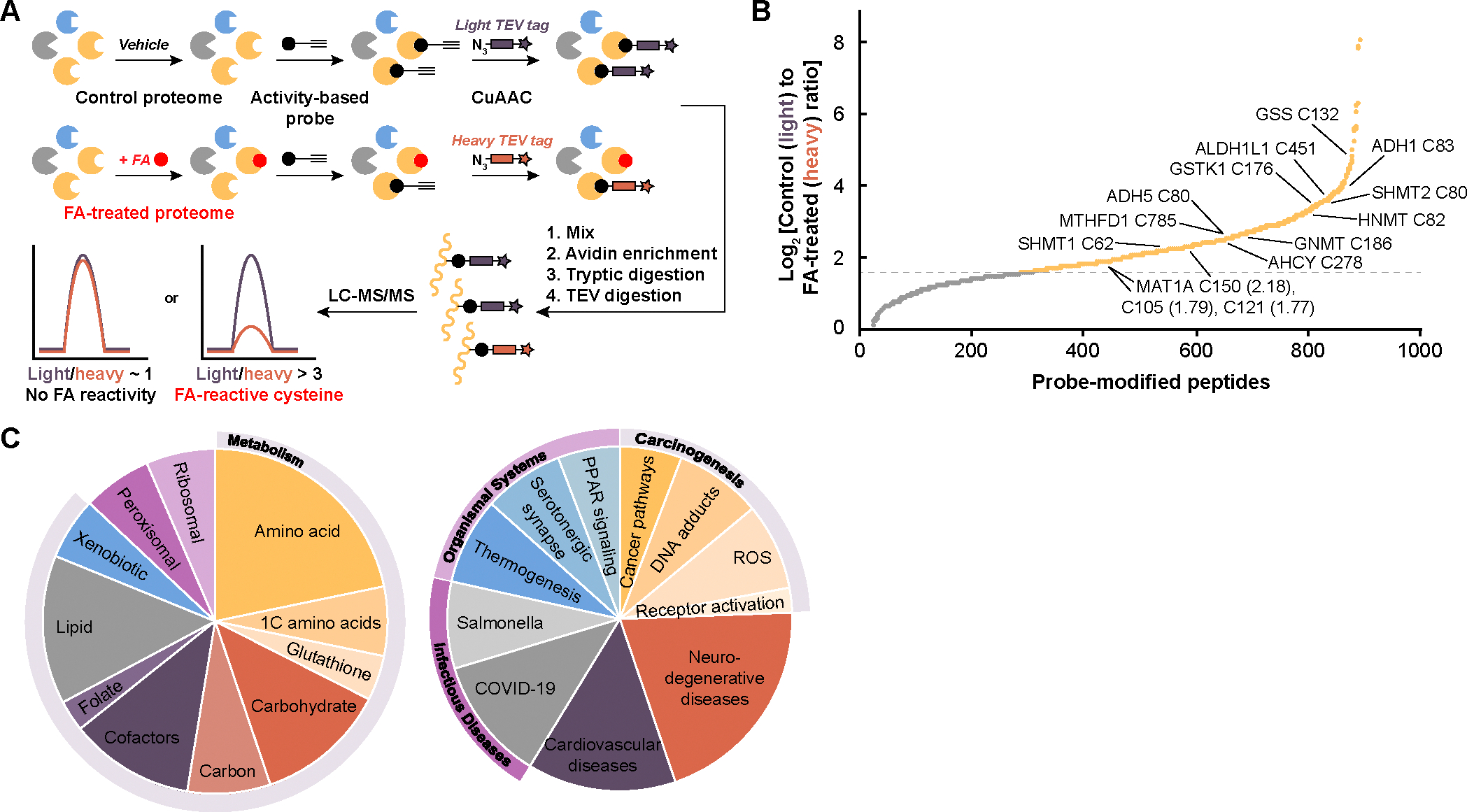
(A) Workflow for isotopic tandem orthogonal proteolysis–activity-based protein profiling (isoTOP-ABPP) analysis of formaldehyde (FA)-sensitive cysteine sites applied to whole proteomes. Mouse liver lysate was treated with vehicle or formaldehyde, followed by iodoacetamide (IA)-alkyne cysteine activity-based probe, labeling of isotopic tags with copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC), downstream digestion, and subsequent analysis of peptide fragments using LC-MS/MS. (B) Waterfall plot of light/heavy ratios of formaldehyde (FA)-sensitive cysteine sites from isoTOP-ABPP (yellow), revealing a pattern of privileged targets for this one-carbon unit. Important enzymes involved in one-carbon and formaldehyde metabolism are labeled with the cysteine residue and MAT1A ratios in parentheses. Gray dotted line represents log2 ratio of 1.58, equivalent to a ratio of 3. Targets were filtered for appearing in at least two technical replicates. (C) Pie chart summarizing the KEGG pathways most abundant with enzymes with ratios greater than 3 for formaldehyde-sensitive cysteines. Pathways were separated into two pie charts by metabolism and cellular processes (308 proteins, left) and organismal systems and diseases (172 proteins, right).
