Fig 9.
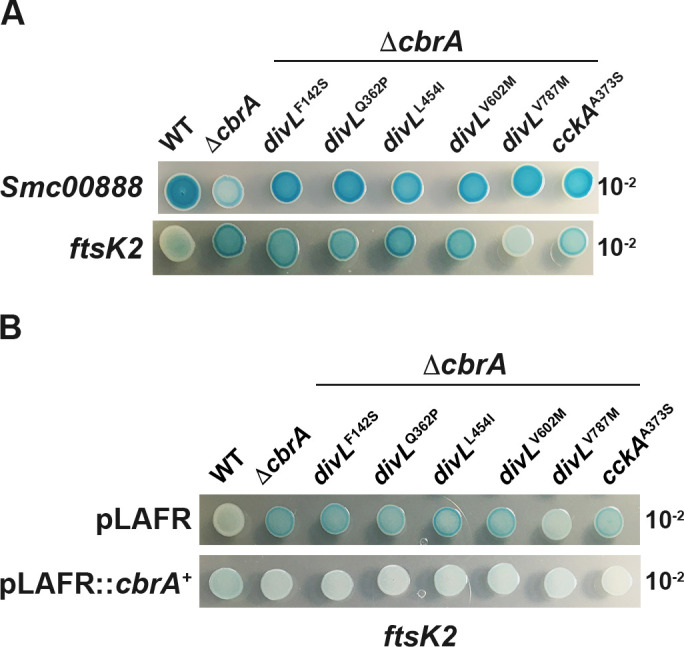
CbrA regulates cell cycle genes through two distinct pathways. Qualitative expression levels of an Smc00888::GUS and ftsK2::GUS transcription fusion were examined using a serial-dilution spot assay on LB/MC media supplemented with an X-GUS indicator dye. (A, top panel) ΔcbrA results in increased expression of Smc00888::GUS relative to wild type, and each divL and cckA allele restores wild-type expression levels. A similar pattern was observed for Smc00887::GUS expression; however, its overall level of activity is significantly decreased relative to Smc00888::GUS (data not shown). (A, bottom panel) The expression of ftsK2::GUS is increased in ΔcbrA; however, this phenotype is not restored to wild-type levels with the exception of divLV787M. (B) CbrA-dependence for ftsK2::GUS expression levels was examined through complementation analysis. (Top panel) With the pLAFR1 empty vector, high-level expression of ftsK2::GUS is observed in each mutant compared to wild type with the exception of ΔcbrA divLV787M. (Bottom panel) In contrast, the presence of pLAFR1::cbrAWT restores wild-type expression in each mutant background.
