Figure 6.
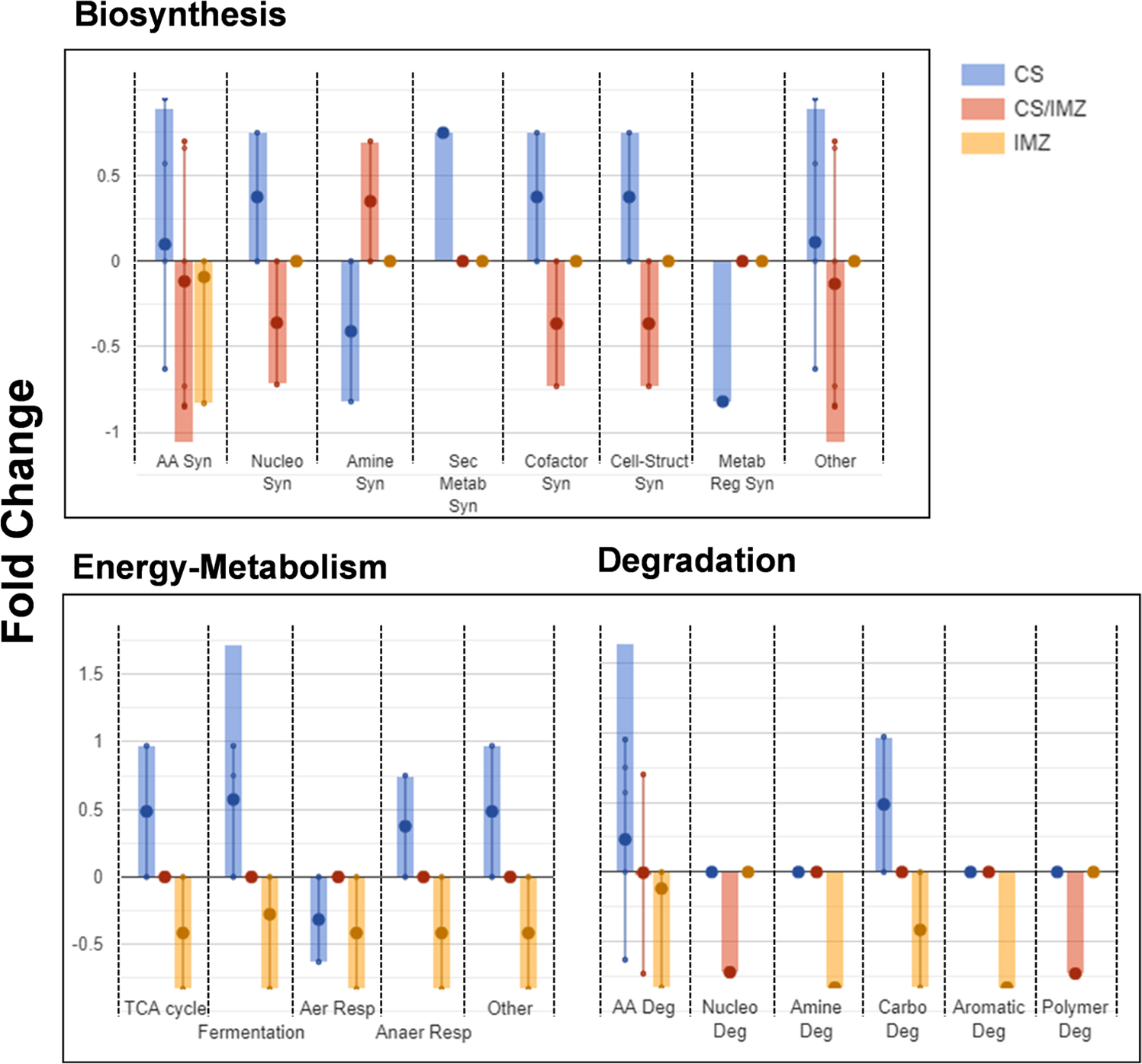
Pathway enrichment due to metabolomics changes. Three major pathways related to citrus clementine were plotted based on the relative changes in the metabolomics due to either cold storage (CS, blue), IMZ treatment (IMZ, orange), or common between both CS and IMZ (CS/IMZ, red). Pathway enrichment for three major pathways, biosynthesis, energy, and degradation, was plotted along with bar plots highlighting the more specific pathways. The y-axis of the plots are the relative fold-change in each experimental condition, with the error bars’ relative representation generated by the CitrusCyc database. Biosynthesis pathways include amino acid synthesis (AA Syn), nucleotide synthesis (Nucleo Syn), amine synthesis (Amine Syn), secondary metabolite synthesis (Sec Metab Syn), cofactor synthesis (Cofactor Syn), cell-structure synthesis (Cell-Struct Syn), metabolite regulation synthesis (Metab Reg Syn), and others. Energy metabolism pathways include tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), fermentation, aerobic respiration (Aer Resp), anaerobic respiration (Anaer Resp), and others. Degradation pathways include amino acid degradation (AA Deg), nucleotide degradation (Nucleo Deg), amine degradation (Amine Deg), carbohydrate degradation (Carbo Deg), aromatic degradation (Aromatic Deg), and polymer degradation (Polymer Deg).
