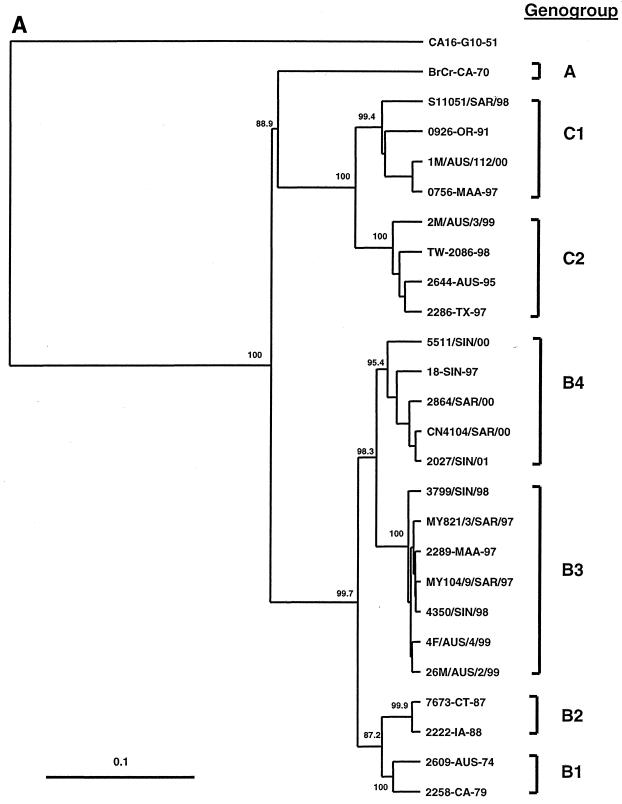
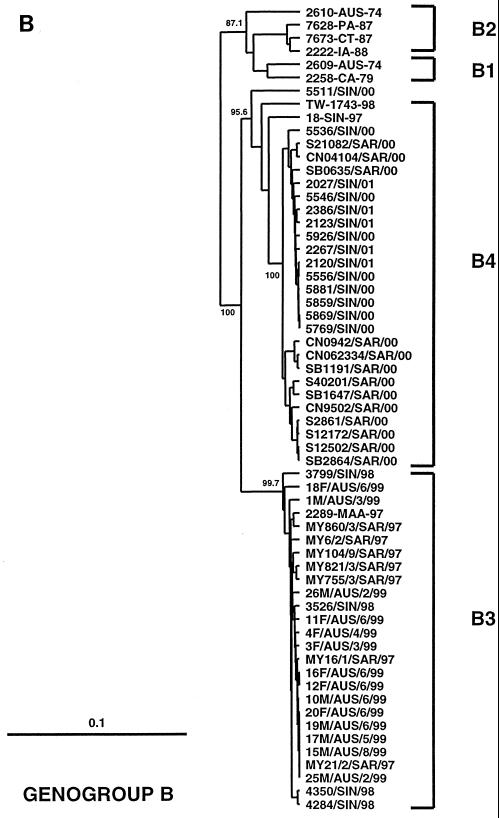
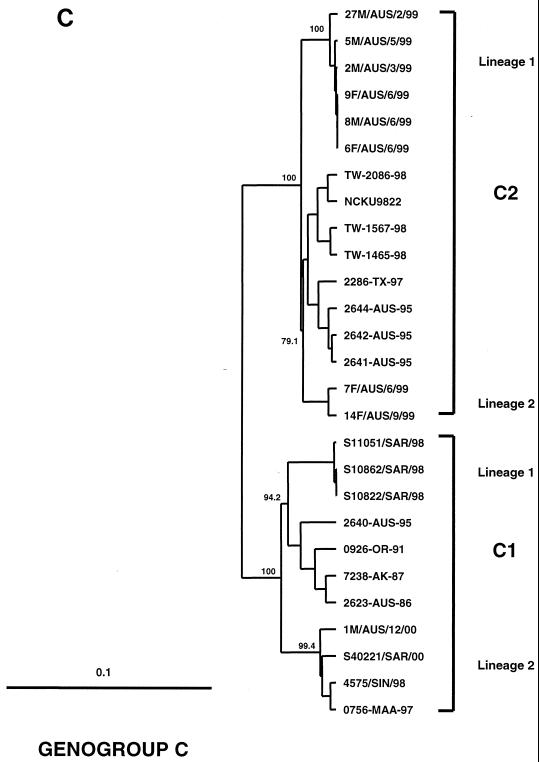
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic trees showing genetic relationships among 66 EV71 field isolates based on alignment of the complete VP1 gene sequence (nucleotide positions 2442 to 3332). Branch lengths are proportional to the number of nucleotide differences. Most strain names indicate a unique number/country or U.S. state of isolation/year of isolation. The trees were constructed by neighbor joining using the Kimura two-parameter distance method (17). The bootstrap values in 1,000 pseudoreplicates for major lineages within the tree are shown as percentages. The marker denotes a measurement of relative phylogenetic distance. In panels B and C, the branches for genogroup A (BrCr-CA-70) and the outgroup (CA16-G10-51) have been removed from the dendrograms to save space. (A) Simplified dendrogram showing genogroups A, B, and C identified by Brown et al. (2). (B) Detailed dendrogram of strains belonging to genogroup B. (C) Detailed dendrogram of strains belonging to genogroup C.