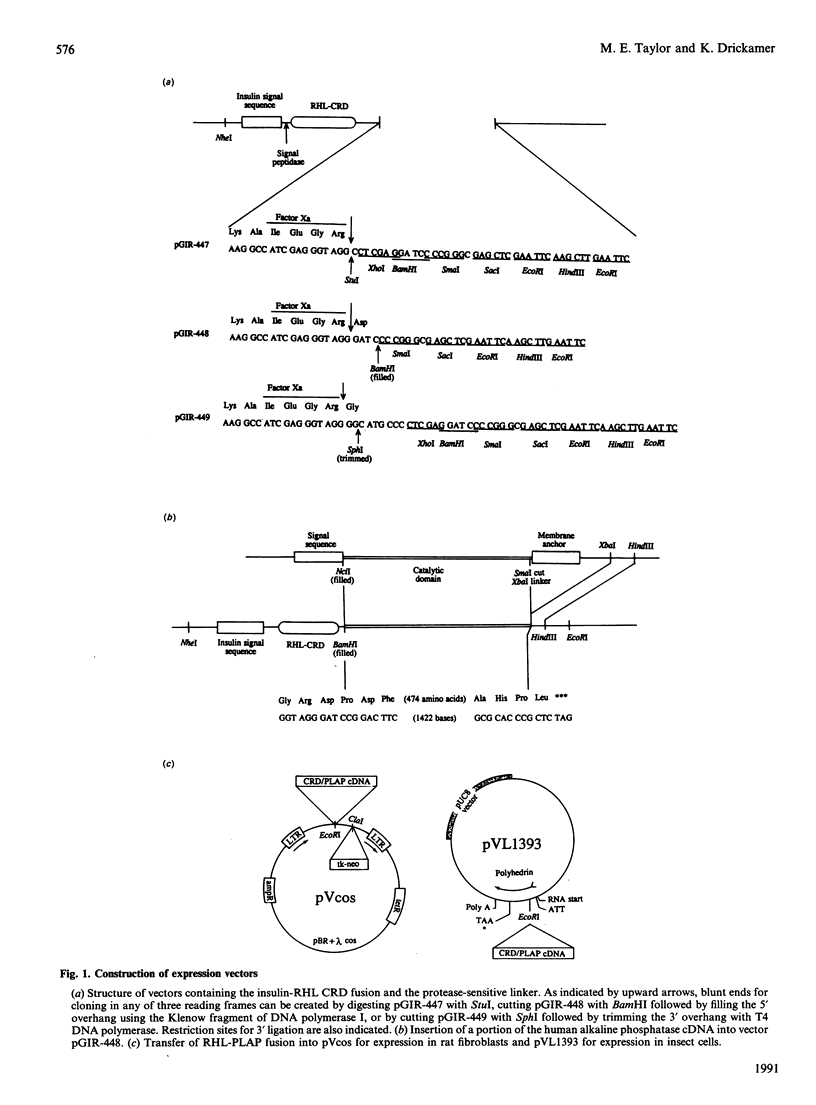
Abstract
Methods have been developed for expression and purification of eukaryotic proteins by creating fusions with the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) of the galactose-specific rat hepatic lectin. In order to generate the fusion proteins, vectors have been constructed so that cDNAs for passenger proteins can be inserted in any reading frame following a segment of DNA encoding the CRD. The feasibility of using this approach as an aid to protein purification has been demonstrated using human placental alkaline phosphatase. Following expression in either of two different eukaryotic expression systems, the CRD-phosphatase fusion protein can be isolated by one step of affinity chromatography on galactose-Sepharose under mild, non-denaturing conditions. Incorporation of a proteinase-sensitive linker allows cleavage of the CRD from the passenger protein. Immobilised proteinase could be rapidly separated from the cleavage products and the released, active phosphatase was purified away from the CRD by re-chromatography on galactose-Sepharose. These methods provide a means of isolating correctly folded recombinant eukaryotic proteins when cDNAs are available, but the properties of the encoded proteins are unknown.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Demonstration of carbohydrate-recognition activity in diverse proteins which share a common primary structure motif. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Feb;17(1):13–15. doi: 10.1042/bst0170013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Multiple subfamilies of carbohydrate recognition domains in animal lectins. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;145:45-58, discussion 58-61. doi: 10.1002/9780470513828.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornstedt N., Porath J. Characterization studies on a new lectin found in seeds of Vicia ervilia. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. J., Sussman H. H. Human placental alkaline phosphatase: molecular weight and subunit structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 26;160(2):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Collins P. M., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. Human serum amyloid P component, a circulating lectin with specificity for the cyclic 4,6-pyruvate acetal of galactose. Interactions with various bacteria. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):107–111. doi: 10.1042/bj2250107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Drickamer K. Signal recognition particle mediates the insertion of a transmembrane protein which has a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Leung J. O., Drickamer K. Rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor lacks a cleavable NH2-terminal signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7338–7342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
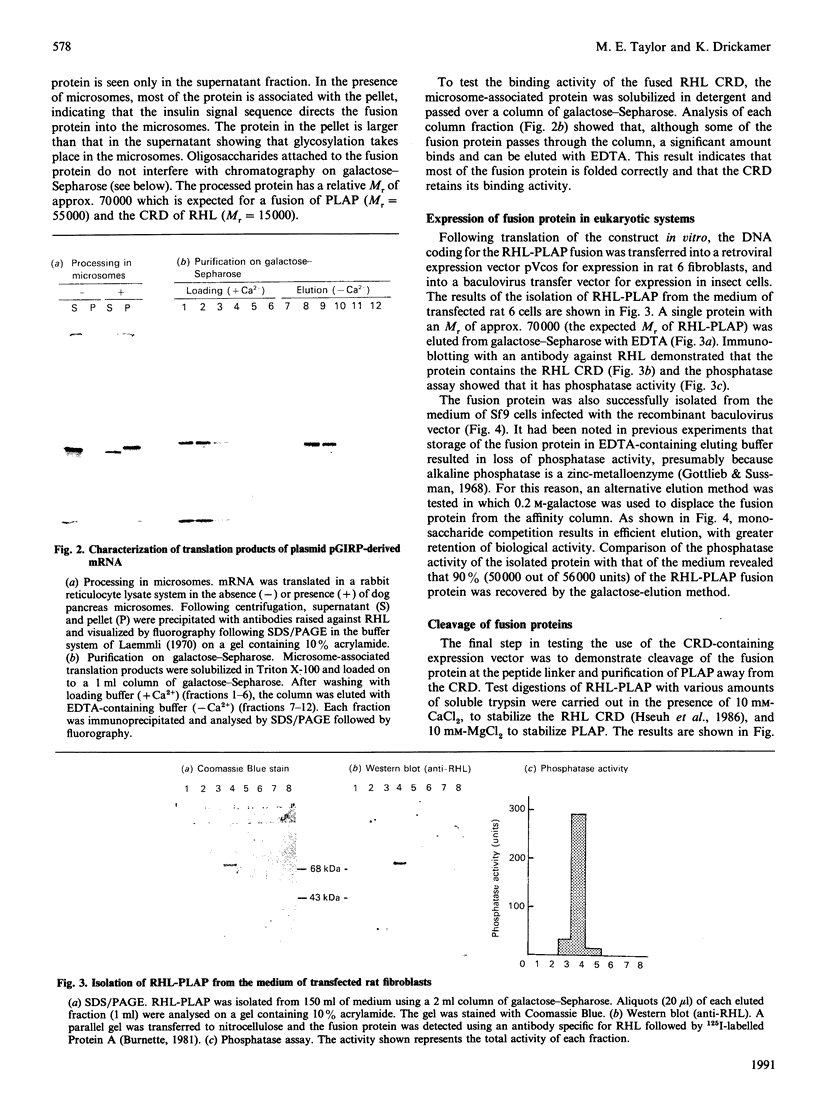
- Hsueh E. C., Holland E. C., Carrera G. M., Jr, Drickamer K. The rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor polypeptide must be inserted into a microsome to achieve its active conformation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4940–4947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the dog insulin gene. Coded amino acid sequence of canine preproinsulin predicts an additional C-peptide fragment. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2357–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
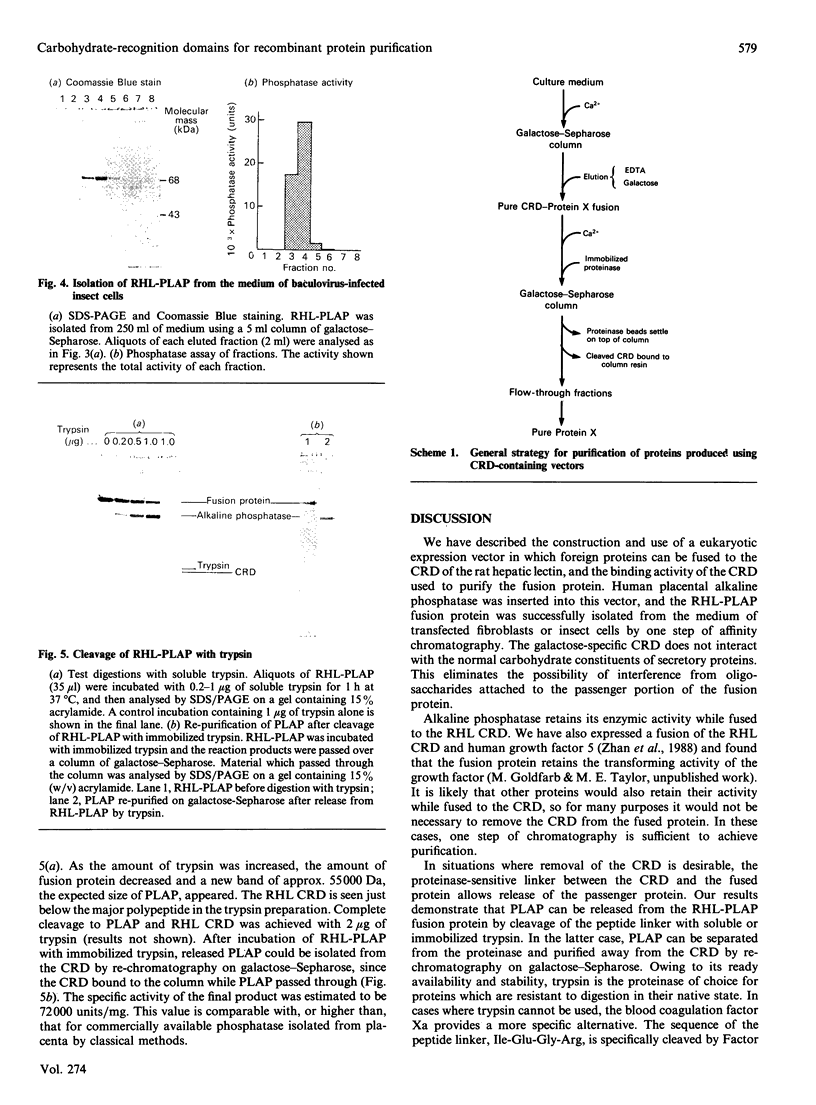
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Generation of beta-globin by sequence-specific proteolysis of a hybrid protein produced in Escherichia coli. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):810–812. doi: 10.1038/309810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Labeling of proteins with beta-galactosidase by gene fusion. Identification of a cytoplasmic membrane component of the Escherichia coli maltose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Guan C., Li P., Riggs P. D., Inouye H. Vectors that facilitate the expression and purification of foreign peptides in Escherichia coli by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]