FIGURE 1.
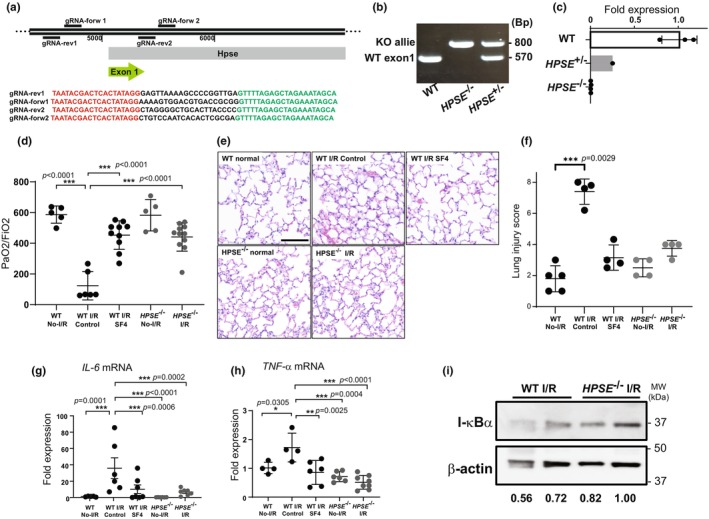
The effect of heparanase‐1 (HPSE) on lung ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury in wild‐type (WT) and HPSE −/− mice. (a) The strategy used to develop HPSE −/− mice using Crispr‐Cas9 and gRNA sequences. (b) PCR genotyping and (c) real‐time PCR quantitation of mRNA expression for the HPSE gene in the lungs of WT, HPSE +/−, and HPSE −/− mice. The left lungs after 1 h of ischemia followed by 4 h of reperfusion were evaluated for injury based on (d) PaO2/FiO2, (e, f) H&E staining/injury score, mRNA expression levels for proinflammatory cytokines (g) interleukin‐6 (IL‐6) and (h) tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α), and (i) western blotting for inhibitor of nuclear factor κB α (ΙκBα) expression. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. WT No‐I/R, uninjured lungs from wild‐type mice; WT I/R control, lungs from wild type mice after 1 h ischemia/4 h reperfusion; WT I/R SF4, lungs from wild type mice pretreated with HPSE inhibitor followed by 1 h ischemia/4 h reperfusion; HPSE −/− No‐I/R, uninjured lungs from HPSE −/− mice; HPSE −/− I/R, lungs from HPSE −/− mice after 1 h ischemia/4 h reperfusion.
