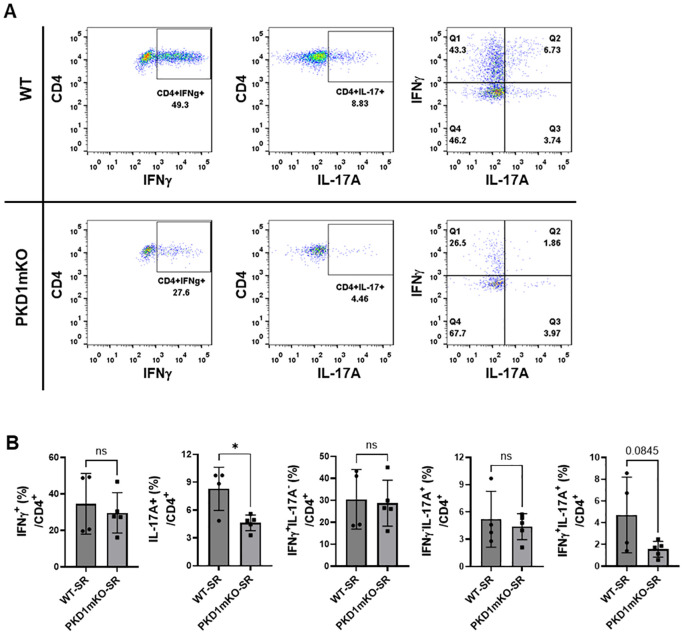
Figure 9.
Effects of myeloid lineage cell-specific PKD1 on Th1/Th17 cell accumulation in the lungs following repeated exposures to S. rectivirgula. PKD1 fl/fl mice (WT) and PKD1 fl/fl -LyZ Cre mice (PKD1mKO) were exposed intranasally to SR (100 μg) three times per week for 3 weeks. Seventy-two hours after the last S. rectivirgula challenge, LICs were collected. LICs were stimulated with PMA plus ionomycin and then processed for intracellular IL-17A and IFNγ detection as described in Materials and Methods. Stained LICs were then subjected to flow cytometric analysis. (A) Gating of CD4+ T cells for IFNγ and/or IL-17A expression. (B) The frequency of IFNγ+, IL-17A+, IFNγ+IL-17A- cells (Q1), IFNγ+IL-17A+ cells (Q2), or IFNγ-IL-17A+ cells (Q3) in the CD4+ T-cell population is expressed as % in the CD4+ cell population. Data represent the mean ± SD. Significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. Statistically significant differences are indicated (*p < 0.05). ns, not significant. Each symbol represents individual mouse. Number of mice used for each group is as follows: WT-SR, n = 4; PKD1mKO-SR, n = 5.