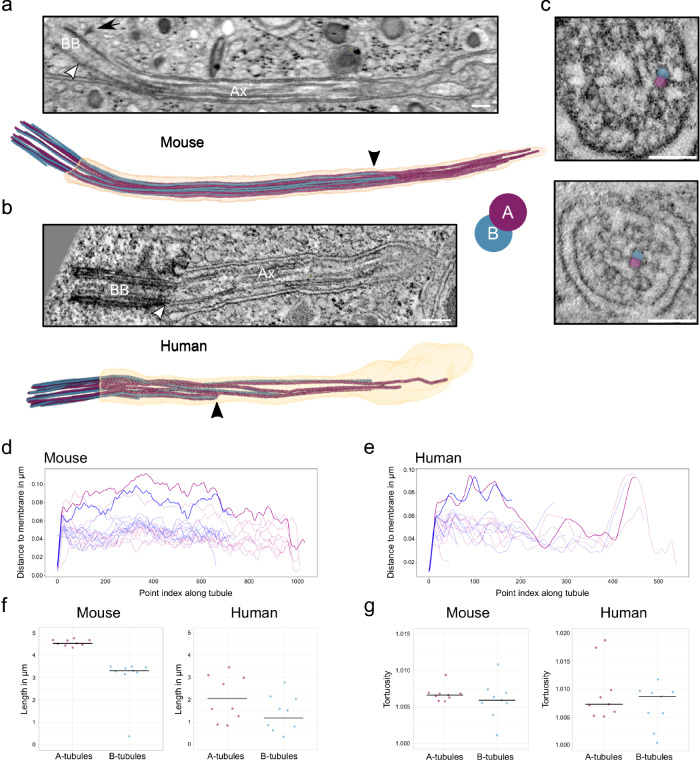
Fig. 2. The axoneme structure of primary cilia of mouse and human beta cells.
a FIB-SEM slice through one mouse beta cell primary cilium. White arrowhead indicates the termination of the basal body, black arrow indicates a distal appendage. BB: basal body, Ax: axoneme. Scale bar: 200 nm. Below is the corresponding 3D rendering with ciliary membrane (light orange), A-tubules (purple), and B-tubules (blue). The black arrowhead points to the termination of a B-tubule. b ssET slice through one human beta cell primary cilium. The white arrowhead indicates the termination of the basal body. BB basal body, Ax axoneme. Scale bar: 200 nm. The 3D rendering shows a human beta cell primary cilium from ssET volumes. The black arrowhead points to the termination of a B-tubule. c Displacement of microtubule doublets to the center of one human beta cell cilium. A- and B-tubules of the example doublet are highlighted in purple (A) and blue (B). Scale bar: 100 nm. d Distance of the microtubules of the mouse beta cell primary cilium to the cilium membrane. Doublets with a major transition are highlighted. e Distance of the microtubules of the human beta cell primary cilium to the cilium membrane. Doublets with a major transition are highlighted. f Length distributions of A- and B-tubules in respective segmentations of one mouse and one human beta cell primary cilium. g Tortuosity of A- and B-tubules in respective segmentations of one mouse and one human beta cell primary cilium. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.