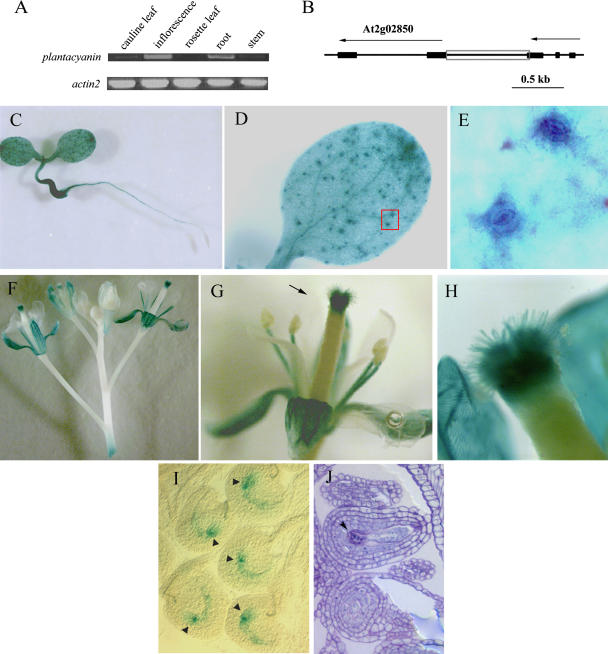
Figure 1.
Expression patterns of Arabidopsis plantacyanin revealed by RT-PCR and transgenic lines expressing GUS driven by the Arabidopsis plantacyanin promoter region. A, Equal amounts of total RNA (1.2 μg) extracted from different plant organs were used as the starting material for RT-PCR. Thirty cycles were carried out for PCR amplification. Actin2 was amplified as a control. B, The plantacyanin promoter region (821 bp; gray box) was amplified by PCR for the plantacyanin promoter-GUS construct. Exons are represented by black boxes and introns by lines. Arrows indicate the orientation of the gene. The Arabidopsis plantacyanin protein ID is At2g02850. C to E, GUS expression in 10-d-old seedlings grown on Murashige and Skoog medium. GUS expression was detected in the whole seedling, except the root apical meristem (C). E, Enlarged view of D, red box showing guard cells. F to H, GUS expression was detected in the reproductive tissues. In addition to sepals and stamen filaments, GUS signals were strongly expressed in the stigma/style, starting from flower stage 11 (when stigma papillae begin to elongate; data not shown) and showing the highest level at stage 13 (G; when pollination occurs). H, Enlarged view of the style shown in G (arrow). No GUS signal was found in mature anther and pollen. I and J, GUS signal also appeared in the mature embryo sac. Arrows are at the chalazal end of the embryo sac. A toluidine blue-stained section (J) shows a longitudinal view of the mature embryo sac.