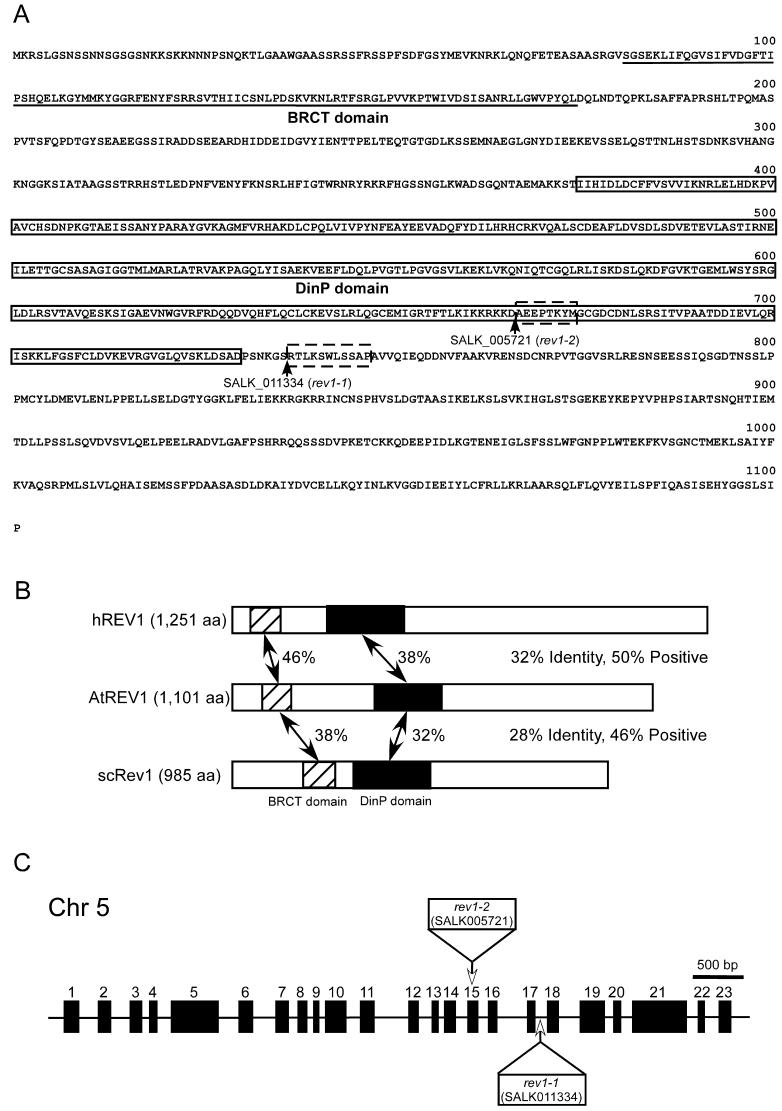
Figure 1.
Structure of AtREV1 cDNA and T-DNA insertion lines. A, Deduced amino acid sequence of AtREV1 cDNA. Underlined sequence indicates the BRCT domain. Boxed sequence of AtREV1 indicates the DinP domain. Arrowheads show T-DNA insertion sites of SALK_005721 (rev1-2) lines and SALK_011334 (rev1-1) lines. Boxed sequences with broken line are amino acids that are predicted to be deleted due to the T-DNA insertion. B, Schematic representation of the alignment of hREV1, AtREV1, and yeast Rev1p (scREV1). Amino acid sequences were compared by the BLAST search program. Regions with significant identity are hatched or shaded (containing the BRCT and DinP domain, respectively), and percent identity is indicated between AtREV1 and other REV1 proteins. C, Structure of the AtREV1 gene and T-DNA insertion sites. Black rectangles represent 23 exons of the AtREV1 gene. White rectangles and arrows indicate the T-DNA insertion positions in exon 15 (rev1-2) and intron 17 (rev1-1). In rev1-1, a 131-bp deletion of genomic DNA was found around the junction of intron 17 and exon 18. In rev1-2, a 23-bp deletion was found in exon 15. The left border sequences were found at both sides of the inserted T-DNA, and T-DNA was accompanied by the insertion of filler DNA aattaggacg and g on the both sides.