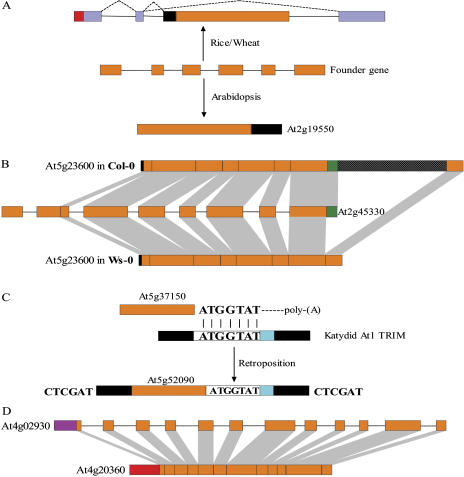
Figure 5.
A, A possible retropositional event occurred before the divergence of monocots and eudicots that had a distinct outcome. Light purple boxes represent exons of the target gene where retroposon integrated, and dashed lines linking exons indicate alternative splicing isoforms. B, Different performances across Arabidopsis ecotypes on one recent retroposon (At5g23600) integration. Gridded black boxes represent a 369-bp sequence identified in Col-0 that was not included in the corresponding regions of the remaining 12 ecotypes such as Wassilewskija (Ws-0), where only a 27-bp unknown sequence exists. C, An exception to the general retroposition process. At5g52090 is coreverse transcribed with a Katydid-At1 type TRIM element by a 7-bp microhomologous region between mRNA of At5g37150 and this TRIM sequence as anchor site. CTCGAT is the identified TSDs generated upon integration. Black boxes indicate two identical terminal repeats of the TRIM element. D, An ambiguous intronless gene that was not retroposon. The intronless translation elongation factor EF-Tu (At4g20360) was a nuclear transfer product of the chloroplast tufA gene, rather than a retroposed copy of the multiple exonic paralog (At4g02930, 12 exons) that encoded the mitochondrial precursor. Red and purple boxes represent the chloroplast and mitochondrial transit peptides of genes, respectively.