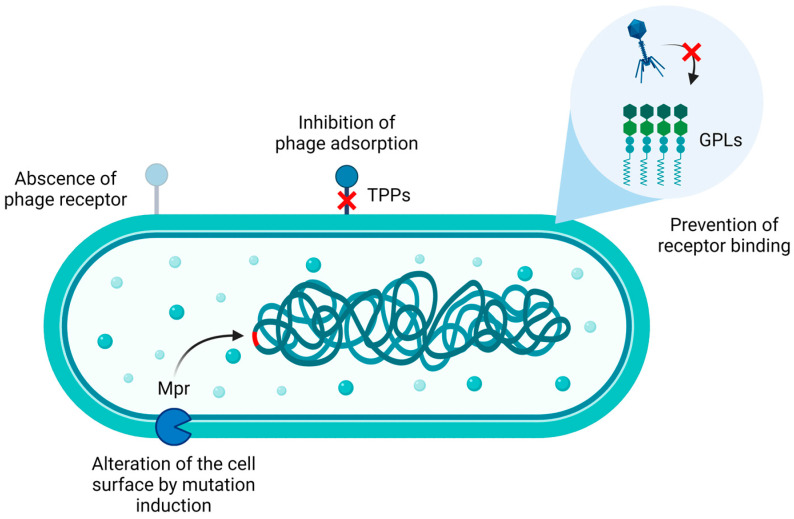
Figure 2.
Phage resistance mechanisms in M. abscessus and M. smegmatis may involve the absence of phage receptors, mutations in phage receptors/co-receptors such as trehalose polyphleates (TPPs) [43], the presence of glycopeptidolipids (GPLs) [44,45], and the induction of mutations in the bacterial genome, eventually altering its surface and impairing phage adsorption, as in the case of the exonuclease Mpr [46,47]. Image created with BioRender.com.