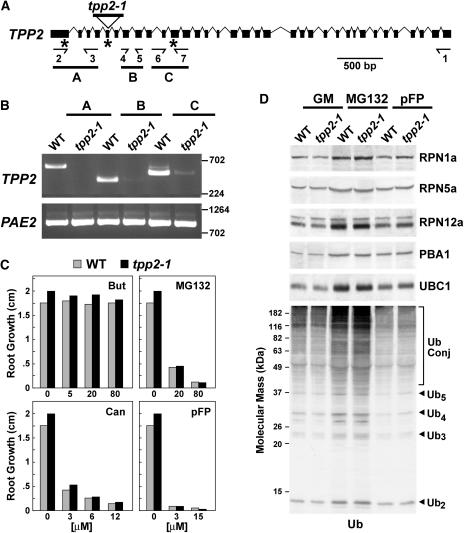
Figure 5.
Genomic and phenotypic descriptions of the Arabidopsis tpp2-1 mutant. A, Gene structure of Arabidopsis TPP2. Coding region and introns are indicated by boxes and lines, respectively. The positions of the T-DNA in tpp2-1 and the locations of the primer pairs used for RT-PCR are indicated. B, RT-PCR analysis of the tpp2-1 insertion mutants. Total seedling RNA was reverse transcribed with primer 1 (see “Materials and Methods”). The reverse transcribed products were then PCR amplified using the A (primers 2 and 3), B (primers 4 and 5), and C (primers 6 and 7) reactions. RT-PCR of PAE2 was included as a control. C, Root growth of wild-type (gray bars) and homozygous tpp2-1 (black bars) seedlings on various concentrations of butabindide (But), MG132, canavanine (Can), and pFP. D, Immunoblot analysis of crude extracts from wild-type and tpp2-1 seedlings with antibodies against Ub, subunits of the CP (PBA1), RP base (RPN1a), and RP lid (RPN5a and RPN12a) from the 26S proteasome, and UBC1, a Ub-conjugating enzyme. Seven-day-old seedlings were exposed for 7 d on solid GM without or with 50 μm MG132 or 50 μm pFP. The migration position of free Ub, Ub chains containing 2 to 5 Ubs, and Ub conjugates are indicated.