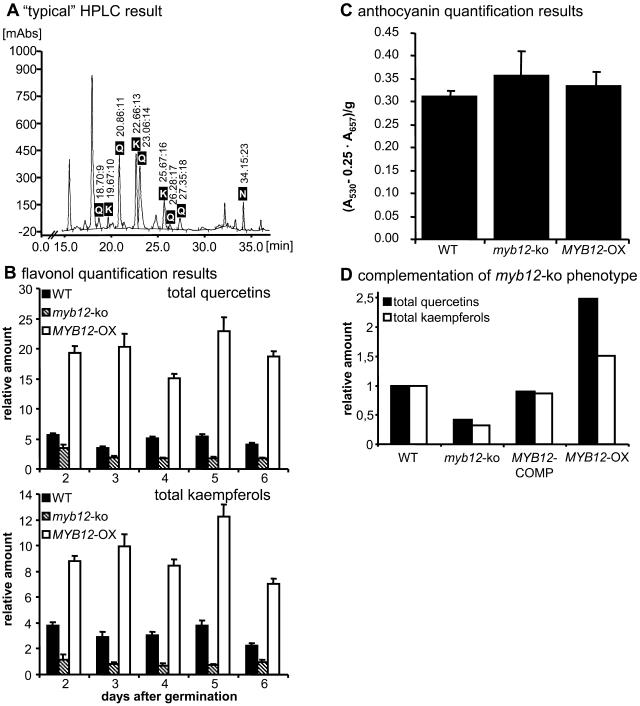
Figure 6.
Biochemical myb12-ko phenotype. A, Representation of a selected HPLC result. The example shows the chromatogram obtained from a methanolic extract of 2-d-old wild-type seedlings. Peaks identified as corresponding to quercetin or kaempferol derivatives and the internal standard naringenin are labeled. Retention times are indicated above the peaks. K, Kaempferol; N, naringenin; Q, quercetin. B, Relative quantification of flavonols (total quercetins and total kaempferols) in methanolic extracts of developing Arabidopsis seedlings by HPLC analysis. The age and the genotype of the seedlings (WT, wild type) analyzed are indicated. Naringenin was used as an internal standard (relative amount arbitrarily set as one). Error bars indicate the sd of the average of relative quercetin/kaempferol amounts determined as triplicates in two independent biological replicates. C, Photometric determination of anthocyanin content in methanolic extracts of 6-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings. A530, Absorption at 530 nm; A657, absorption at 657 nm. Error bars represent the sd of the average from a total of six measurements using two independent biological replicates. D, Complementation of the myb12-ko phenotype by transformation of myb12-ko plants with a 4.5-kb MYB12 genomic fragment. Relative flavonol contents in methanolic extracts of 6-d-old wild-type, myb12-ko, MYB12-COMP, and MYB12-OX plants were determined by HPLC.