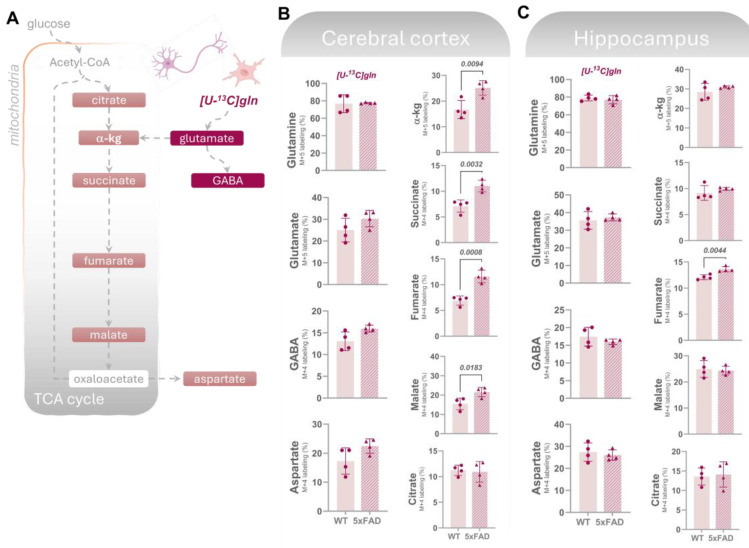
Figure 5.
Glutamine uptake is unchanged while its metabolism is higher in the 5xFAD cortex. (A) Uptake and metabolism of [U-13C]glutamine (gln) gives rise to 13C-enrichment (detected by GC–MS) in glutamate, GABA, and TCA cycle intermediates in acutely isolated slices from (B) cerebral cortex or (C) hippocampus incubated with the labeled substrates for 60 min. 13C-enrichment from direct glutamine metabolism is presented as M + X labeling % (X = number of 13C-carbons in a given molecule). In the cerebral cortex, overall maintained 13C-incorporation in amino acids from [U-13C]gln was observed, while higher labeling was detected in most TCA cycle intermediates in 5xFAD mice compared to wild-type (WT) controls, suggesting increased glutaminolysis. In hippocampal slices, a maintained labeling in amino acids and TCA cycle intermediates resulting from [U-13C]gln metabolism, with the exception of fumarate, was detected in the 5xFAD mice vs. WT. Values represent mean (±) SD (n = 4 animals). WT animals are represented as circles, while 5xFAD animals are represented as triangles. The statistical significance (determined with Student’s unpaired t-test) is presented with p values above the bars, with significant values in bold.