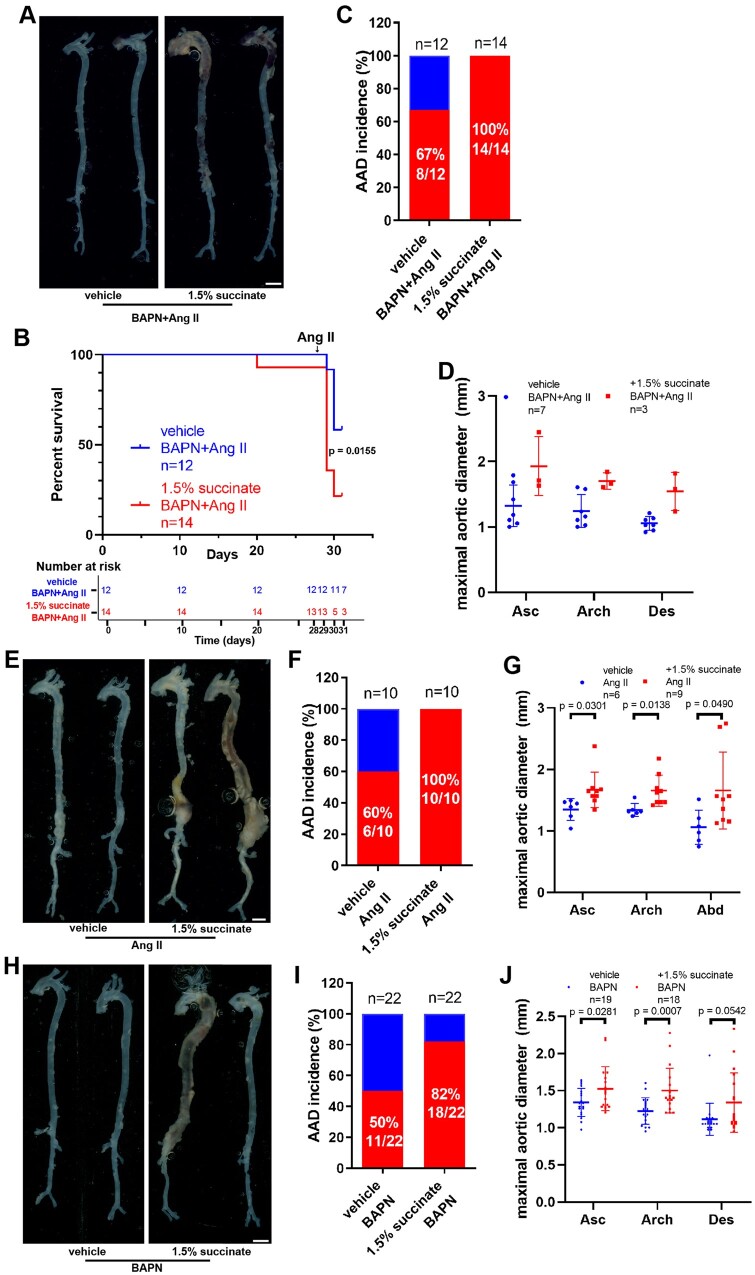
Figure 2.
Supplementation with succinate aggravates aortic aneurysm and dissection in vivo. (A–D) Four-week-old male mice were administered with 0.25% BAPN (wt/vol) for 28 days with or without 1.5% sodium succinate (wt/vol) and then infused with saline or angiotensin II (1000 ng/kg/min) for 3 days: vehicle + BAPN/angiotensin II, n = 12; and 1.5% succinate + BAPN/angiotensin II, n = 14. (A) Representative morphology of the aortas for each group. Scale bar = 2 mm. (B) Survival curve and number at risk, log-rank test. (C) Incidence of aortic aneurysm and dissection for each group. (D) Measurement of the maximal aortic diameter ex vivo. n = 7 for mice administered BAPN/angiotensin II and n = 3 for 1.5% succinate + BAPN/angiotensin II (mice died of aortic rupture were not included). (E–G) Nine-week-old Apoe–/– male mice were infused with saline or angiotensin II (1000 ng/kg/min) for 28 days with or without 1.5% sodium succinate (wt/vol): vehicle + angiotensin II, n = 10; and 1.5% succinate + angiotensin II, n = 10. (E) Representative morphology of the aortas from different groups of mice. Scale bar = 2 mm. (F) Incidence of aortic aneurysm and dissection in different groups of mice. (G) Measurement of the maximal aortic diameter ex vivo. n = 6 for mice administered angiotensin II and n = 9 for 1.5% succinate + angiotensin II (mice died of aortic rupture were not included). H–J, Three-week-old male mice were administered with 0.25% BAPN (wt/vol) for 28 days with or without 1.5% sodium succinate (wt/vol): vehicle + BAPN, n = 22; and 1.5% succinate + BAPN, n = 22. (H) Representative morphology of the aortas from the different groups of mice. Scale bar = 2 mm. (I) Incidence of aortic aneurysm and dissection from the different groups of mice. (J) Measurements of the maximal aortic diameter ex vivo. n = 19 for mice administered BAPN and n = 18 for 1.5% succinate + BAPN (mice died of aortic rupture were not included). Apoe–/–, apolipoprotein E-deficient; Asc, ascending aorta; Des, descending aorta.