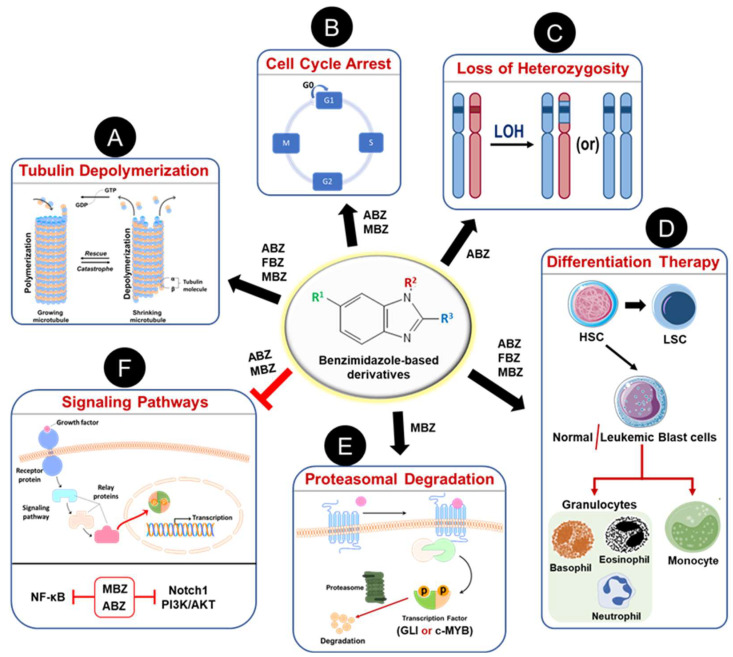
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of action of anthelmintic benzimidazole-based derivatives as anti-leukemic agents. As a classical anthelmintic, BMDZs inhibit tubulin polymerization (A) to induce cell death by mitotic cell arrest (B). Albendazole (ABZ) known to accelerate chromosomal missegregation and thus induces loss of heterozygosity in mammalian cells (C). Some BMDZs are known to induce terminal differentiation of leukemic blast cells to granulocytes and/or monocytes and thus cause cell death (D). Treatment with BMDZs promotes proteasomal degradation of transcriptional factors such as GLI and c-Myb, which play a vital role in leukemia development and progression (E). Also, these BMDZs inhibit several oncogenic signaling pathways (Notch1, PI3K/AKT, NF-κB) to achieve remission during the treatment of hematological malignancies (F).