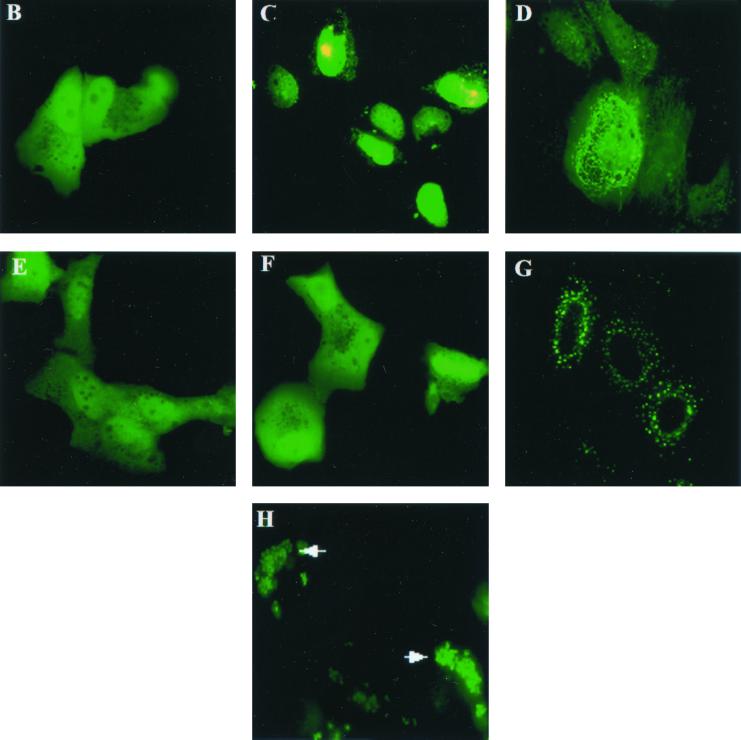
FIG. 3.
Map of the VP22 domain(s) that supports nuclear targeting. (A) Schematic representation of the VP22-GFP constructs used. GFP (shaded boxes) was fused to various domains of VP22 (white boxes) with the start sites and endpoints labeled. D17 cells were transfected with VP22 containing aa 1 to 123 (VP221–123)-GFP (B), VP22118–258-GFP (C), VP22159–258-GFP (D), VP22118–221-GFP (E), VP221–197-GFP (F), VP221–221-GFP (G), or VP22-GFP in the presence of 50 pg of Colcemid per ml (H) and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy directly. Magnification, ×63. Note that the carboxyl terminus of VP22 (C) supports nuclear targeting.