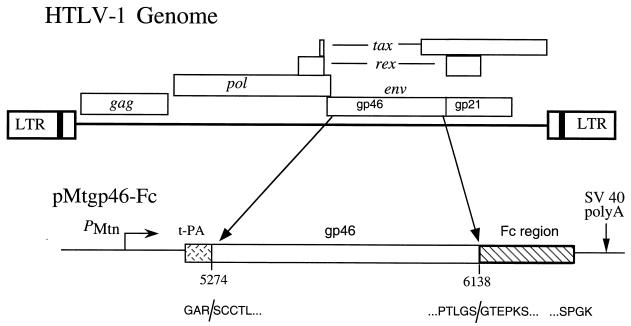
FIG. 1.
Constructs used to express SU-Fc. Shown is a simplified diagram of the HTLV-1 genome illustrating the major genes and highlighting the region used to generate the SU expression constructs. Plasmid pMtgp46-Fc, used to express the HTLV-1 SU-immunoadhesin, and the nucleotide coordinates of the env region used (nucleotide numbering follows that of Seiki et al. [41]) are shown below. At the carboxyl terminus four amino acid codons (RSRR) of SU were replaced by the human IgG Fc domain-coding region. Transcription was driven by the inducible Drosophila metallothionein promoter (PMtn), and the transcripts were terminated by use of the SV40 early polyadenylation sequences. For expression and secretion of the recombinant SU-immunoadhesin, the signal sequence and first four amino acids of the mature SU-coding region were replaced with the 36-amino-acid signal sequence from the human tPA gene. Speckled rectangle, tPA sequences; open rectangle, env sequences; hatched rectangle, human IgG Fc sequences; thin line, vector sequences. The predicted structure of the mature protein products expressed are shown in one-letter amino acid code; three amino acids (GAR), derived from the tPA signal sequence, replace the first four amino acids of SU, and the SU sequences are fused at the carboxyl terminus to sequences derived from Fc.